STEPS
TOOLS
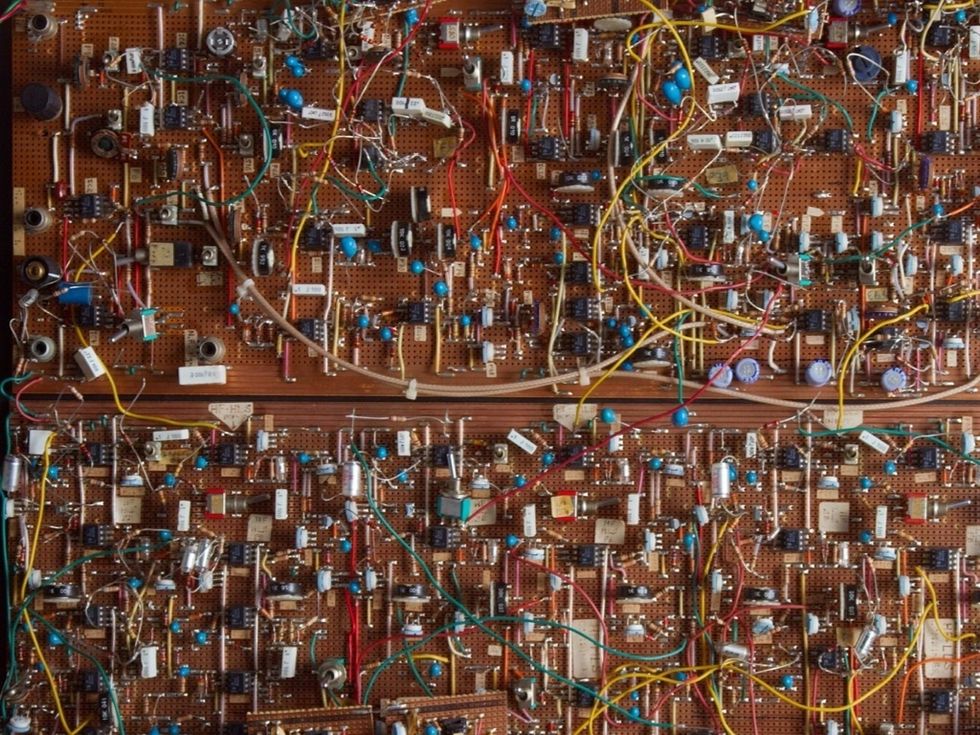

On the inside, electronics look something like THIS?!! That is one busy BREADBOARD!
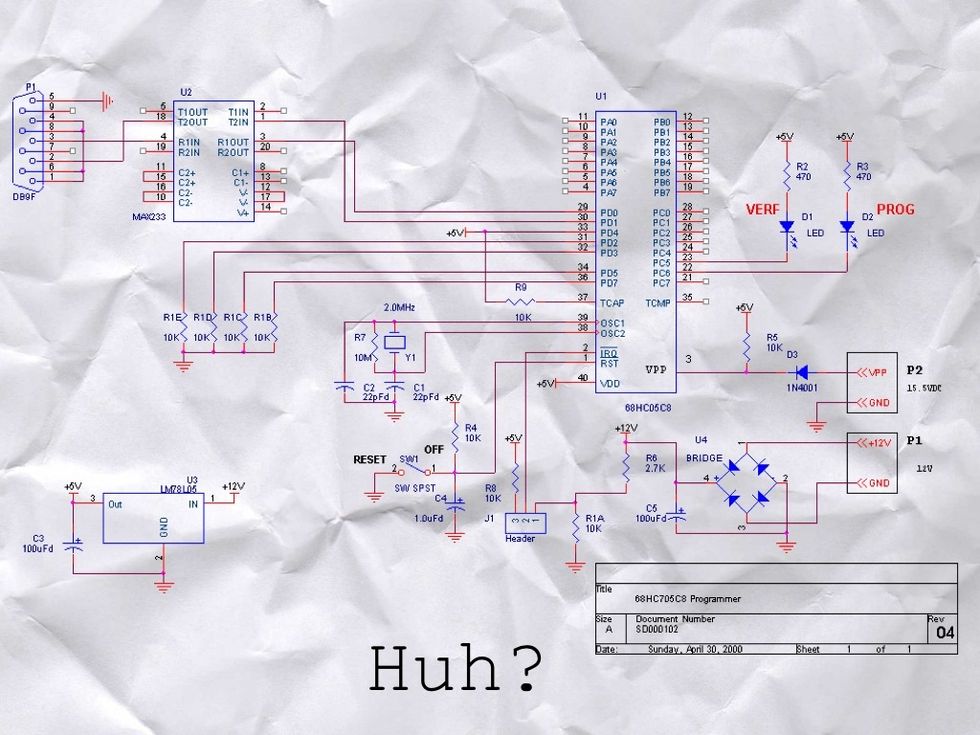
On paper they look something like this. This is called a SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
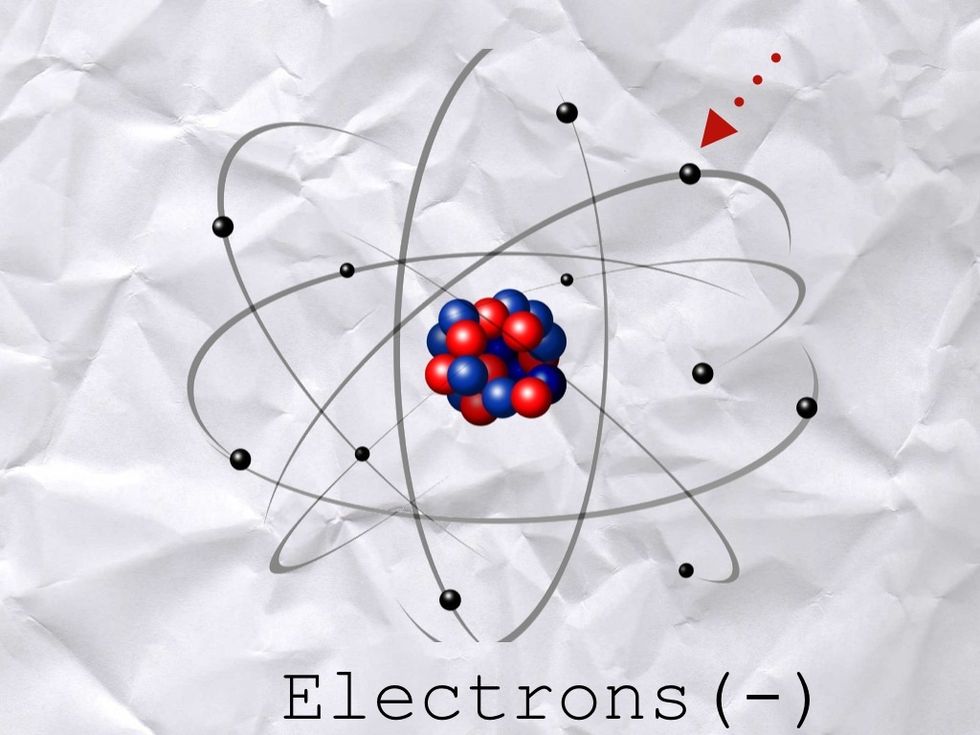
Electronics is all about ELECTRONS which are NEGATIVELY charged particles that float around the NUCLEUS of an ATOM. Chemistry junk.
Electrons are VERY VERY VERY small, and VERY VERY VERY active! And when you have a bunch of them together you get a lot of ENERGY!
SOURCE

This is an ELECTRON PUMP also known as a BATTERY. It pumps out electrons just like a WATER PUMP pumps out water. Water also is made of TINY TINY TINY things. This is the SOURCE of electrons.

The amount of ELECTRON PUMPAGE or PRESSURE a battery can pump is measured in VOLTS. The RATE at which the electrons are pumped is measured in AMPS and the amount of RESISTANCE to pumpage in OHMS.
Electrons have a CURRENT FLOW, just like water has a current flow. Water can take up space and so can electrons. And when it is a tight space you get PRESSURE!

This is a WATER PUMP. The Electron Pump of water.
LOAD

Electrons flow from the SOURCE (Battery )to the LOAD (A LAMP)

Just as a pool has a LOAD OF WATER in it. Water flows from the PUMP to the POOL.
WIRE

And the thing that connects the BATTERY to the LOAD is a WIRE, which determines the SOURCE PATH (The path that the electrons from the source to the load).

Just like a HOSE determines the SOURCE PATH of WATER.
When these three things are connected correctly you then have a COMPLETE CIRCUIT.
If you had a HOLE in your HOSE or a CUT in your WIRE, you would have an OPEN CIRCUIT, and the electrons would not get to the load and the lamp will not work. :(
RESISTOR

Another part of a CIRCUIT is a RESISTOR. A resistor... RESISTS! It resists CURRENT FLOW.

Sorta like a PINCH in a HOSE.
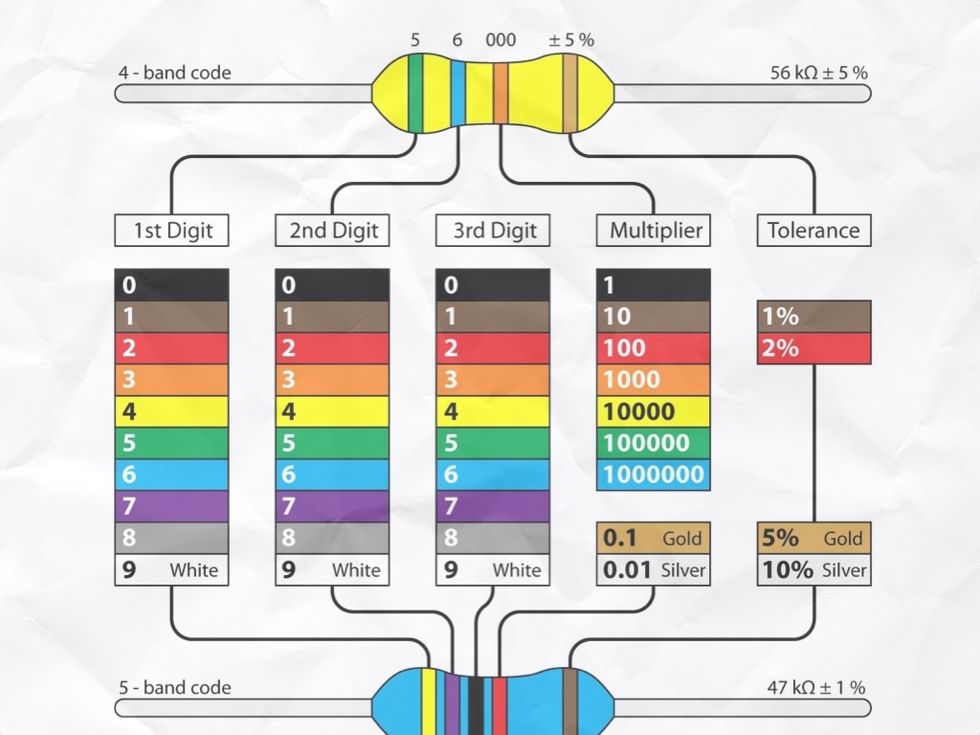
Resistors have COLOR CODED bands on them to tell you how much FLOW they RESIST. A GREEN band(5) followed by a BLUE band(6) then by an ORANGE(3) stands for 56,000 ohms. The third band is a multiplier.
It tells you HOW MANY ZEROS go after the first two bands. The colors are read from the end that doesn't have a gold band towards the gold band. Since Orange=3 that means "3 ZEROS"
There are many things that can resist the flow of water. For example, the material the hose is made out of can resist. Also the size of the hose could cause resistance. It is the same in electronics.
If a wire is not a good CONDUCTOR (If it can't transport electrons well) then it is causing RESISTANCE. Also if the wire is small, it will cause resistance.
Resistors just resist! That is their main thing. But we can gradually change resistance by using a part called a...
POTENTIOMETER

A potentiometer is a metal rod that has a WIPER attached to it. The current flows through the rod up to the WIPER. As you turn the wiper the current either flows more or less.

Sorta like a WATER SPIGOT.
DIODE

Sometimes on the source path you have other parts. One part is a DIODE. A diode is like a ONE WAY GATE.
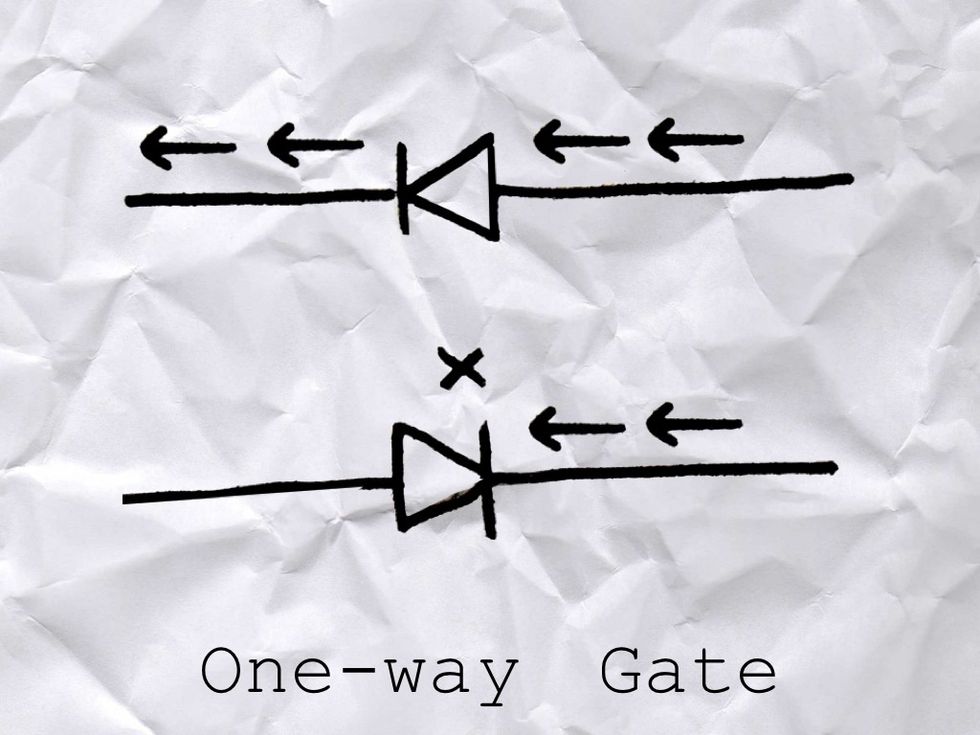
Electrons can flow one way through it, but not the other way. This is how it looks on a schematic diagram. The electrons follow the way the arrow points.
CAPACITOR

These are CAPACITORS. They are like temporary rechargeable batteries. They can HOLD a certain CAPACITY of electrons and they can also DISCHARGE (leak) a certain amount of electrons.

Sorta like a WATER TANK.
TRANSISTOR
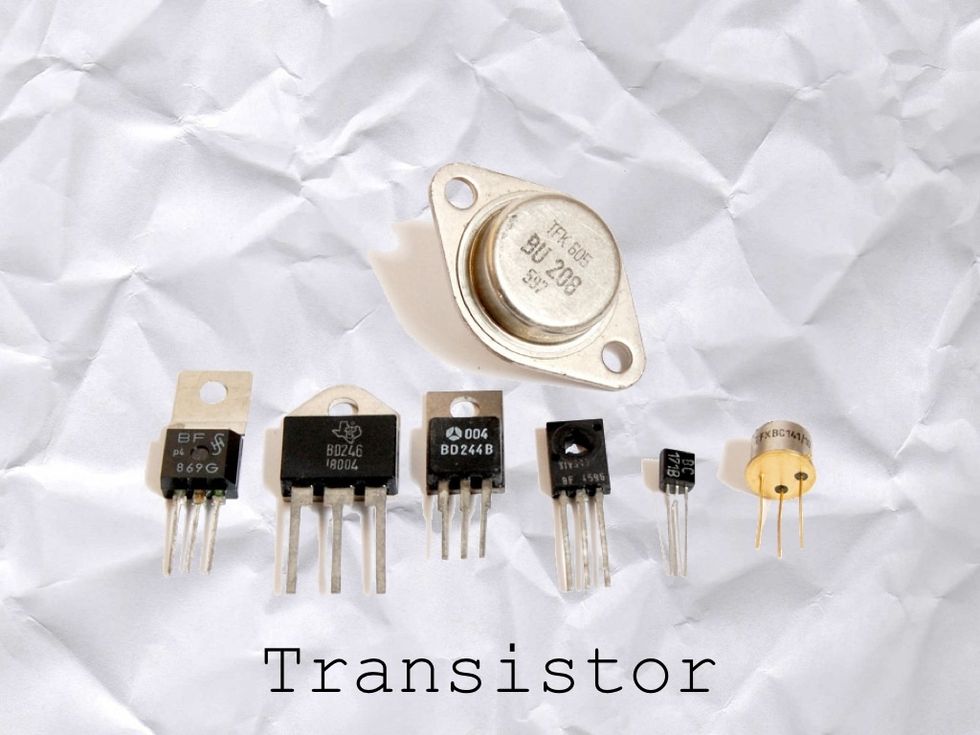
These are TRANSISTORS. They are like switches that CONTROL THE FLOW of electrons. Electrons can go THIS WAY or THAT WAY.

Like a sprinker.
SEMICONDOCTORS
Both diodes and transistors are called SEMICONDUCTORS, because SOMETIMES they conduct (soak up) electrons, and other times they don't. That is how they control the flow.
And there are many other types of Semicondoctors!
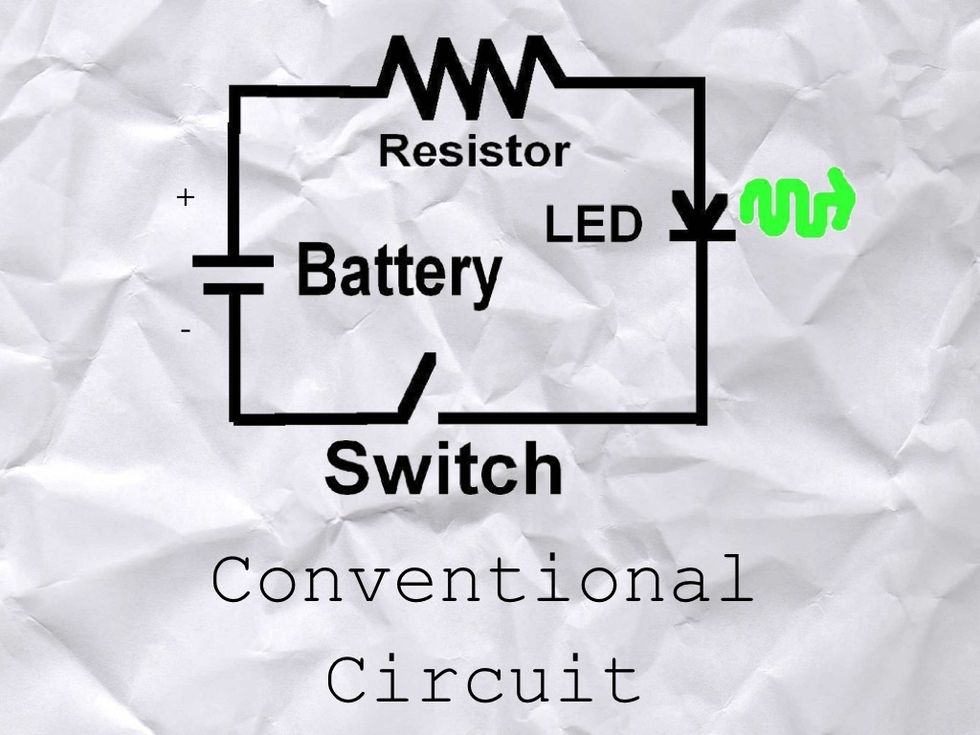
So, electrons flow from the POSITIVE side of the battery, through the load, to the NEGATIVE side of the battery. It might go through a RESISTOR or through a DIODE or through a SWITCH on the way.
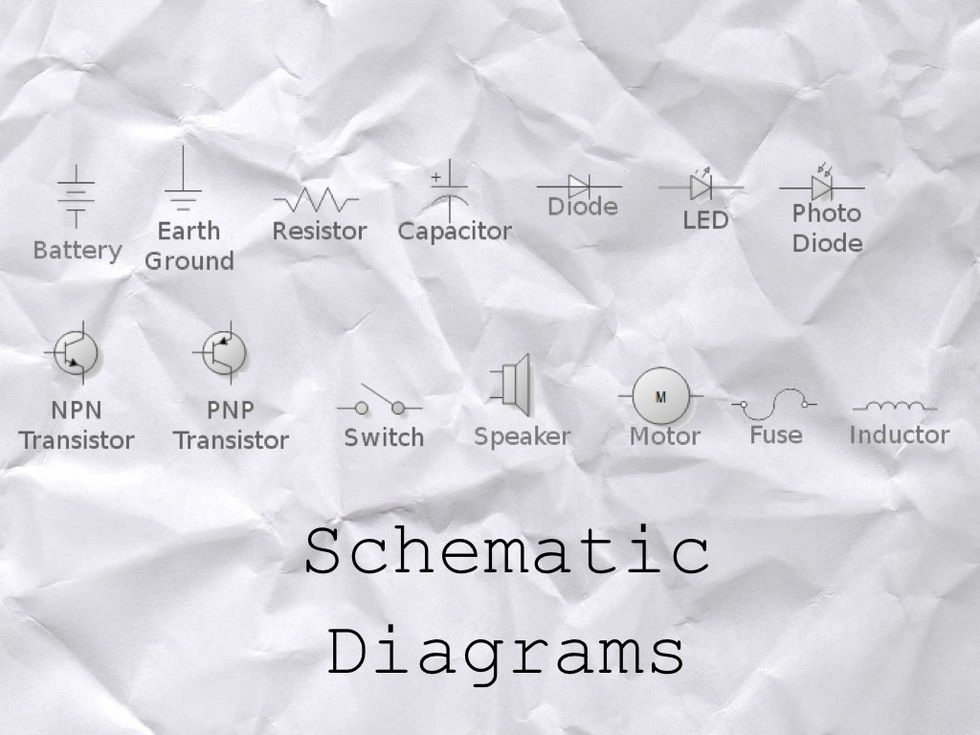
These are a few SCHEMATIC SYMBOLS for different parts of an ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT.
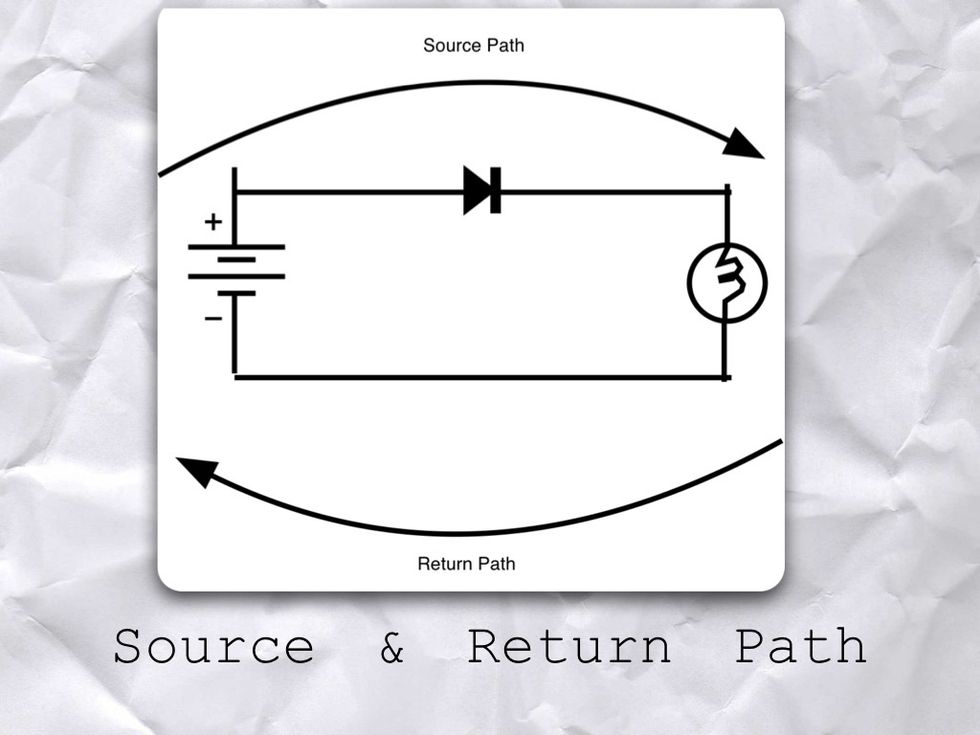
The path from the positive side of the Battery to the load is called the SOURCE PATH. The path from the load to the negative side of the battery is called the RETURN PATH.

But sometimes, before water gets to a pump it comes from the GROUND, as in a RESERVOIR. There is no pressure in the RESERVOIR
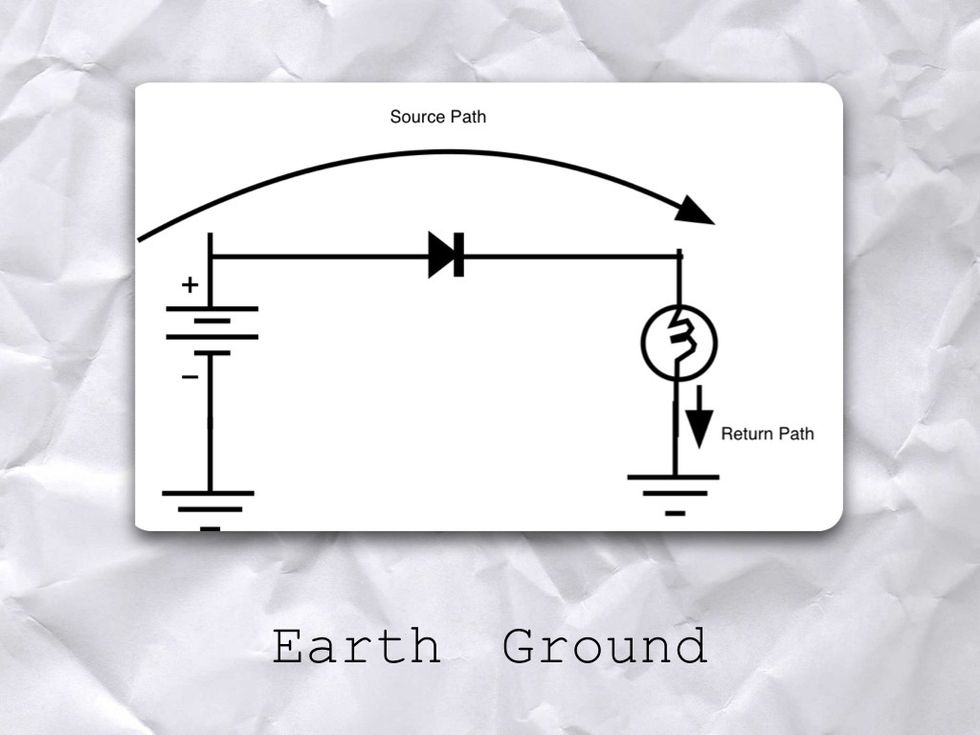
It is the same with electronics. They can be connected directly to the EARTH which has ZERO VOLTS of pressure. Then it is pumped out and through a circuit by a source.
If a circuit is connected to the earth on both ends it is as if the ground itself is the return path.
For example, your wall outlet is connected to EARTH GROUND.
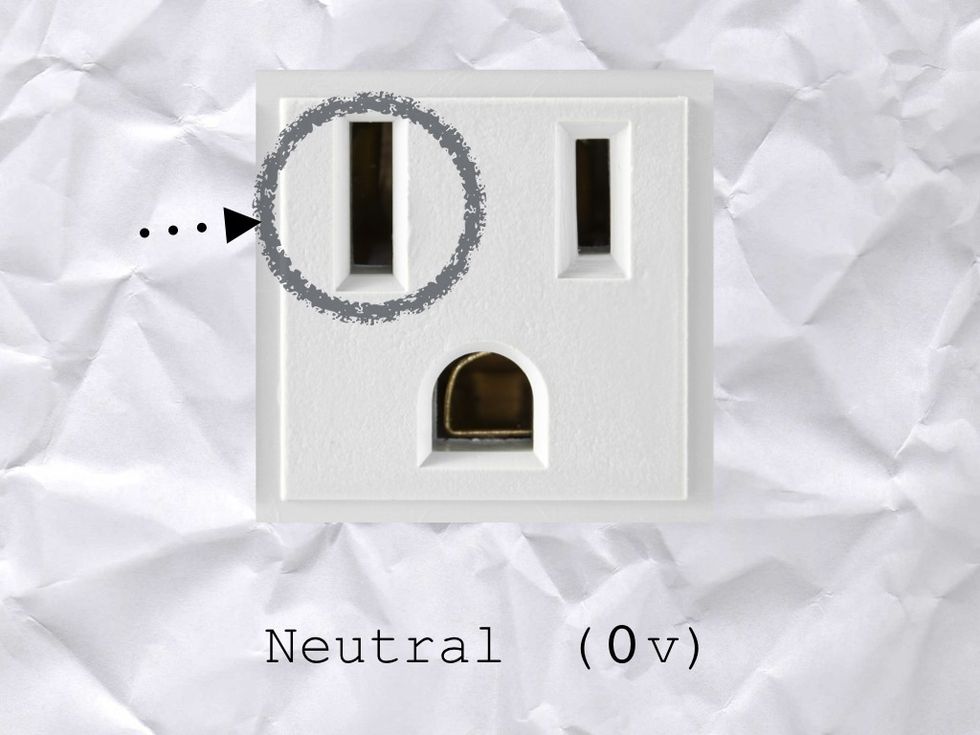

The LONG SLOT is the NEUTRAL slot. It has 0 volts of pressure coming from it

The bottom slot is the part that is connected to EARTH GROUND, which also has 0 volts of pressure coming from it.

small slot is the HOT slot. This is what shocks you!
But what if the circuit is not connected to the ground? Like in the case of CARS?
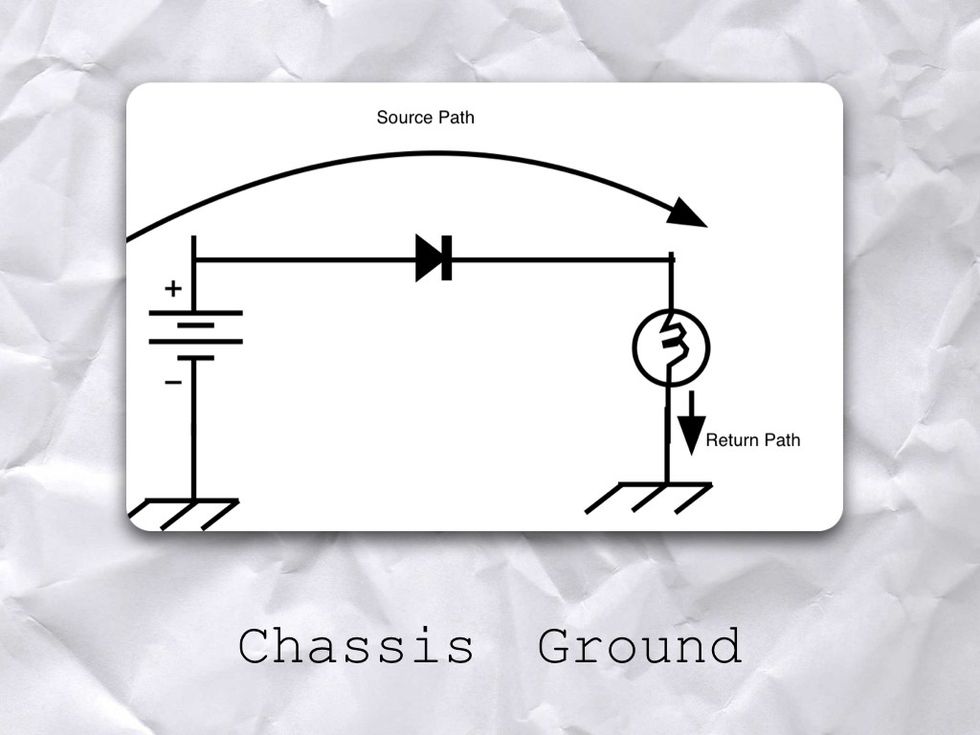
Well any GROUND that is not earth ground is called CHASSIS GROUND.
They have a good reason for calling it that.
But what really causes that bulb to light up or that game to turn on? Well FRICTION! Electrons rubbing each other the wrong way, and it creates HEAT. And from that friction comes LIGHT.
Sound is also caused by friction caused by electrons!
Who said it has to be complicated?
END. :)
You can tinker with a digital electronics simulator right on your iPad with ICIRCUIT by Krueger Systems Inc. ($10)
The creator of this guide has not included tools
The Conversation (0)
Sign Up