How to transmit an action potential along a neuron
Transmit an Action Potential Along a Neuron
44
STEPS
TOOLS
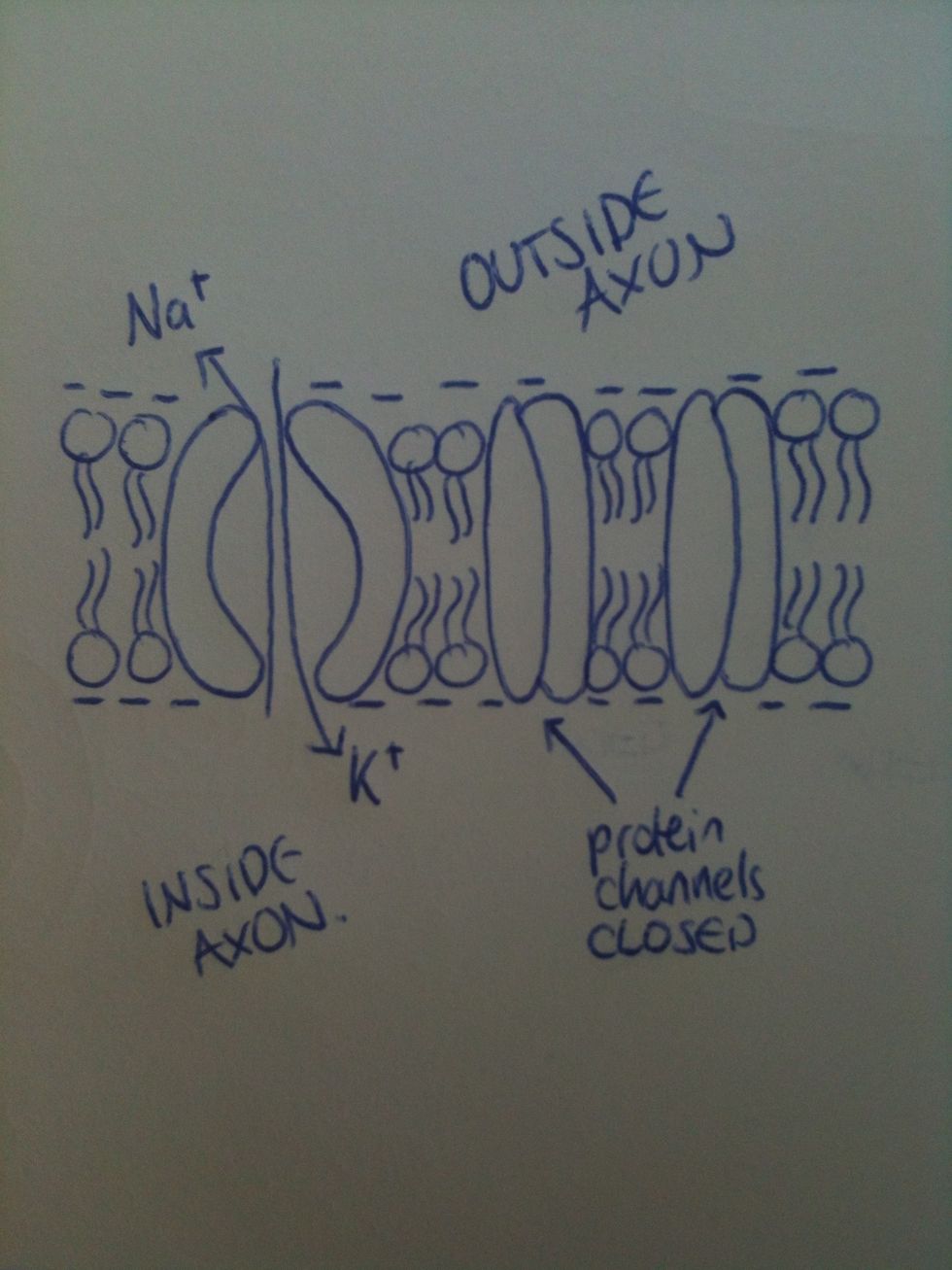
At resting potential, the Na+/K+ pump expels Na+ ions diffusing into the axon, against the conc. gradient. It's an active transport pump that works with ATP, by allowing K+ to enter the axon.

This creates a polarisation; because there are 30x more Na+ molecules outside the axon, there is a positive charge outside and a negative charge inside. The potential difference is -70 millivolts.
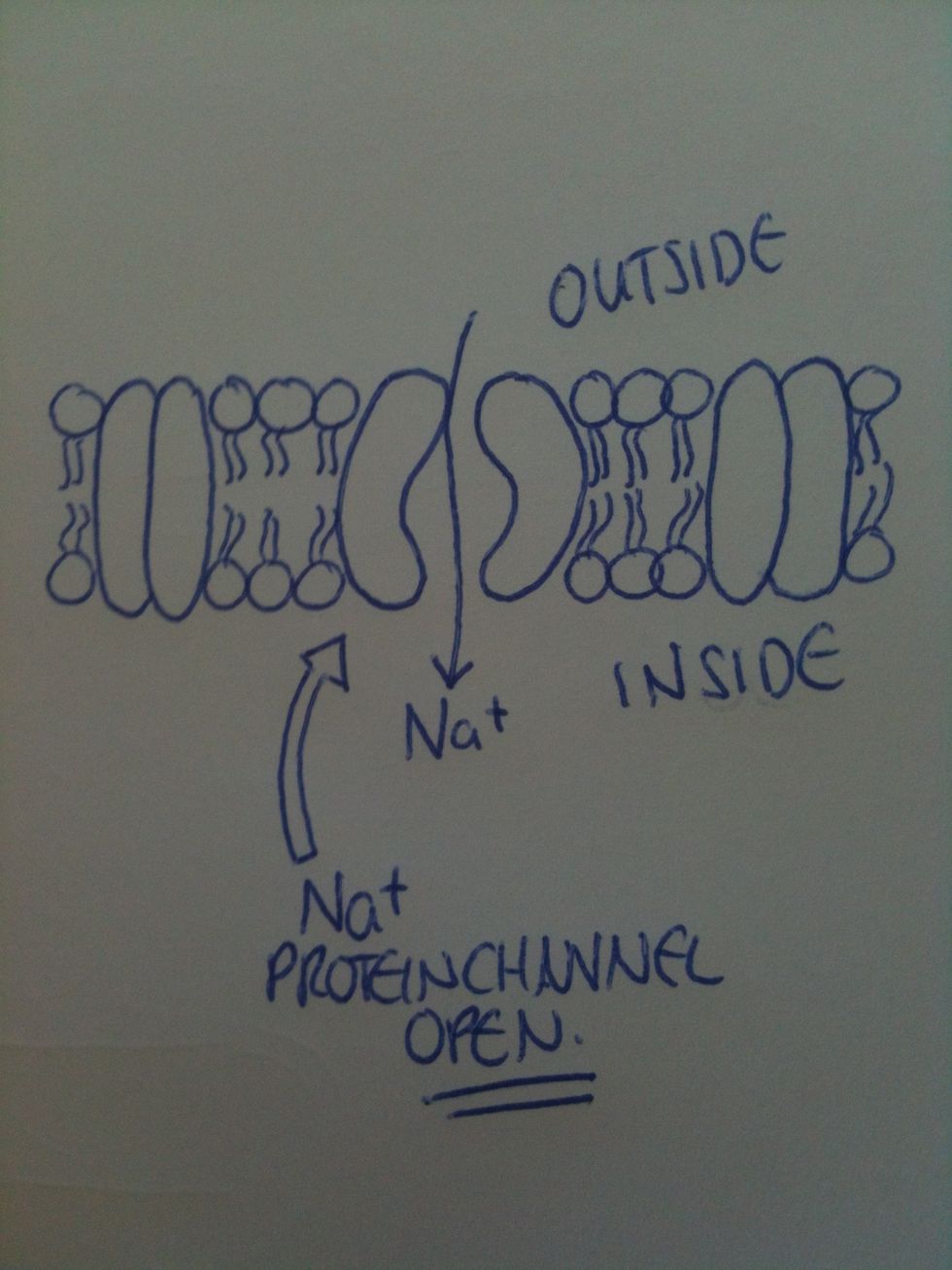
During an action potential, sodium channels open to allow Na+ ions into the axon. The K+ channels remain shut. The concentration of Na+ ions inside the axon increases.
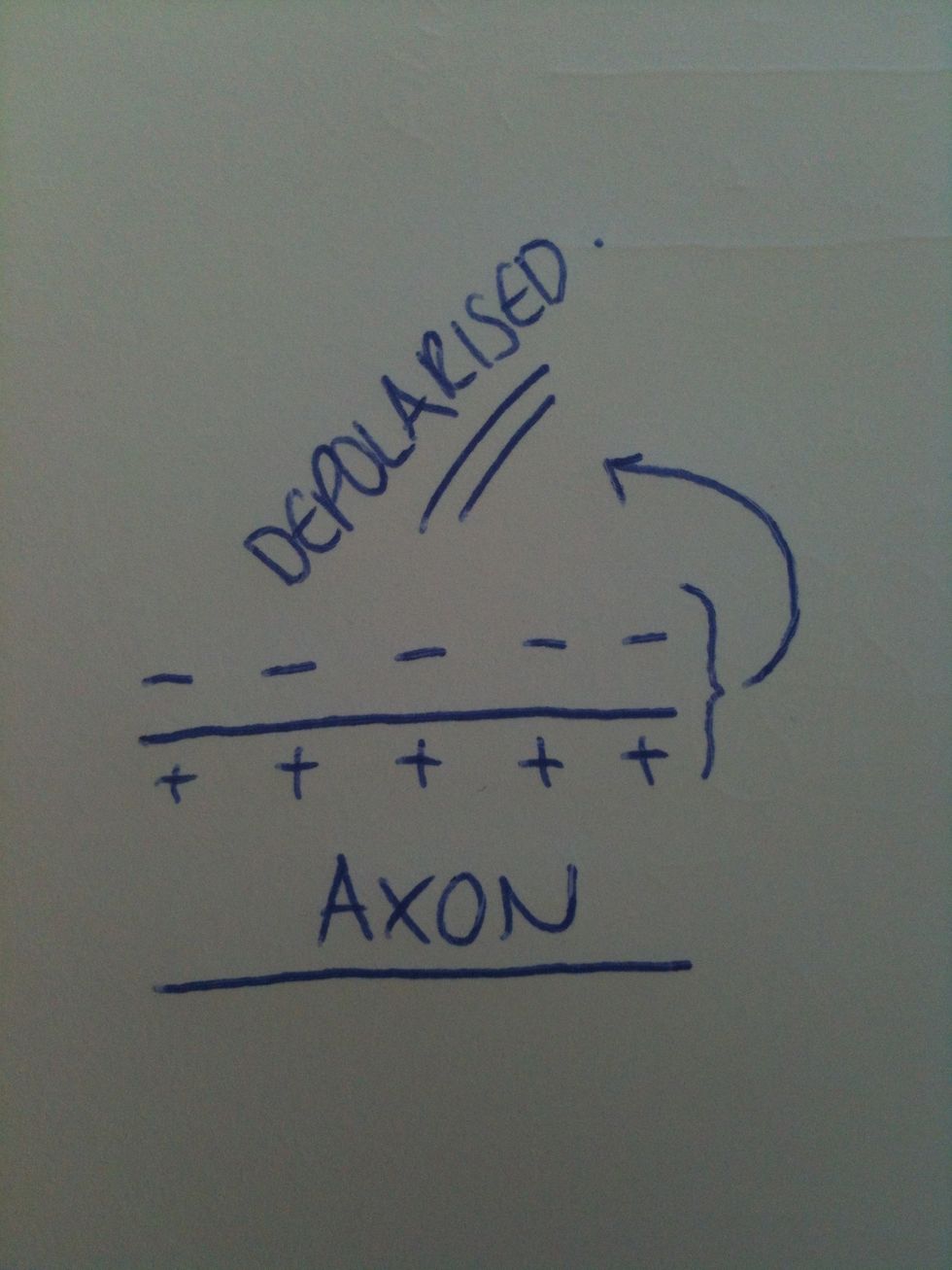
There is now a negative charge on the outside of the axon membrane and a positive charge on the inside of the axon. The potential difference changes to around +50 millivolts.
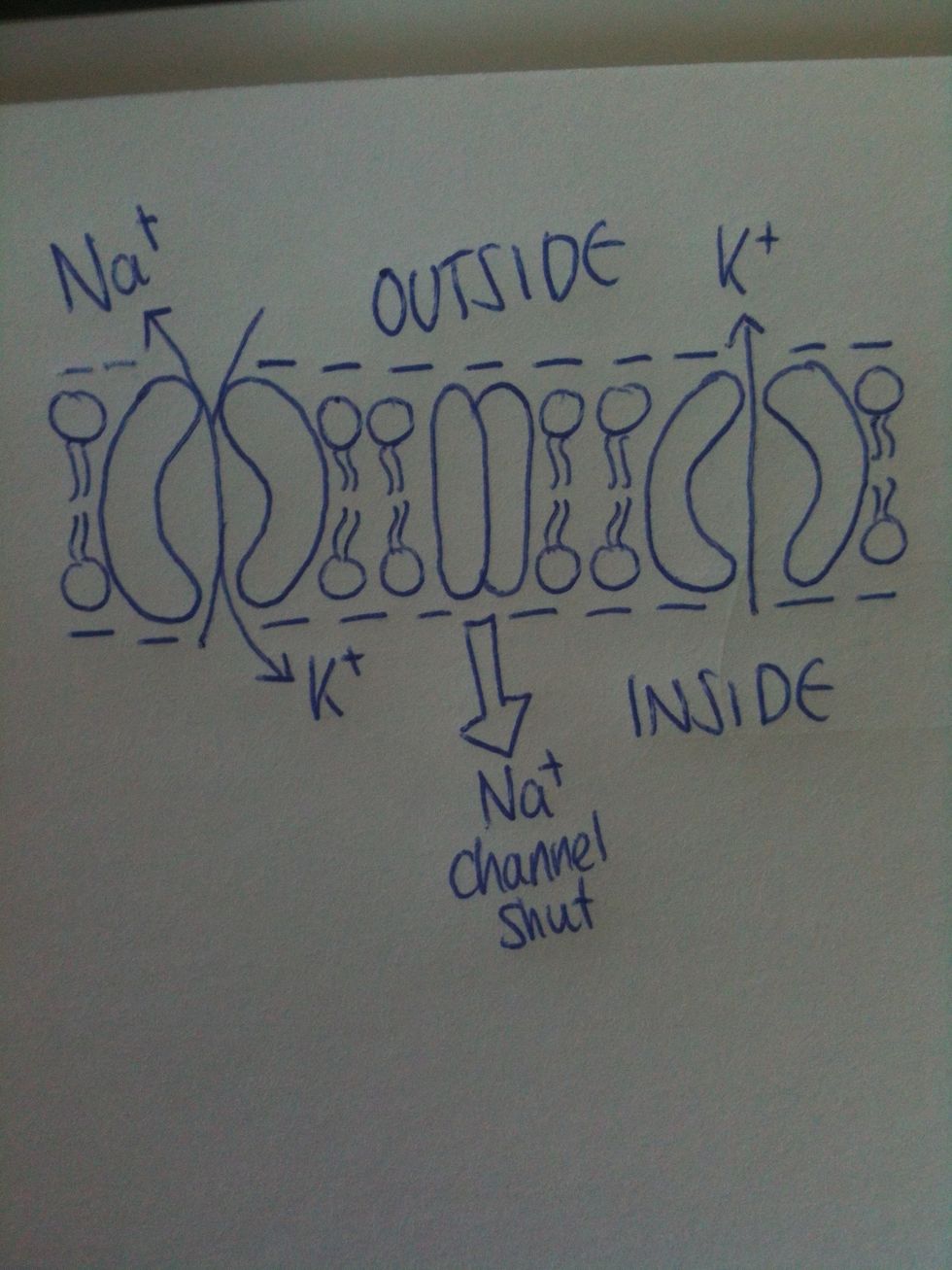
During the repolarisation stage of action potential, a K+ channel opens so K+ ions leave the axon. Any Na+ ions that have entered during the action potential are will be removed by the Na+/K+ pump.
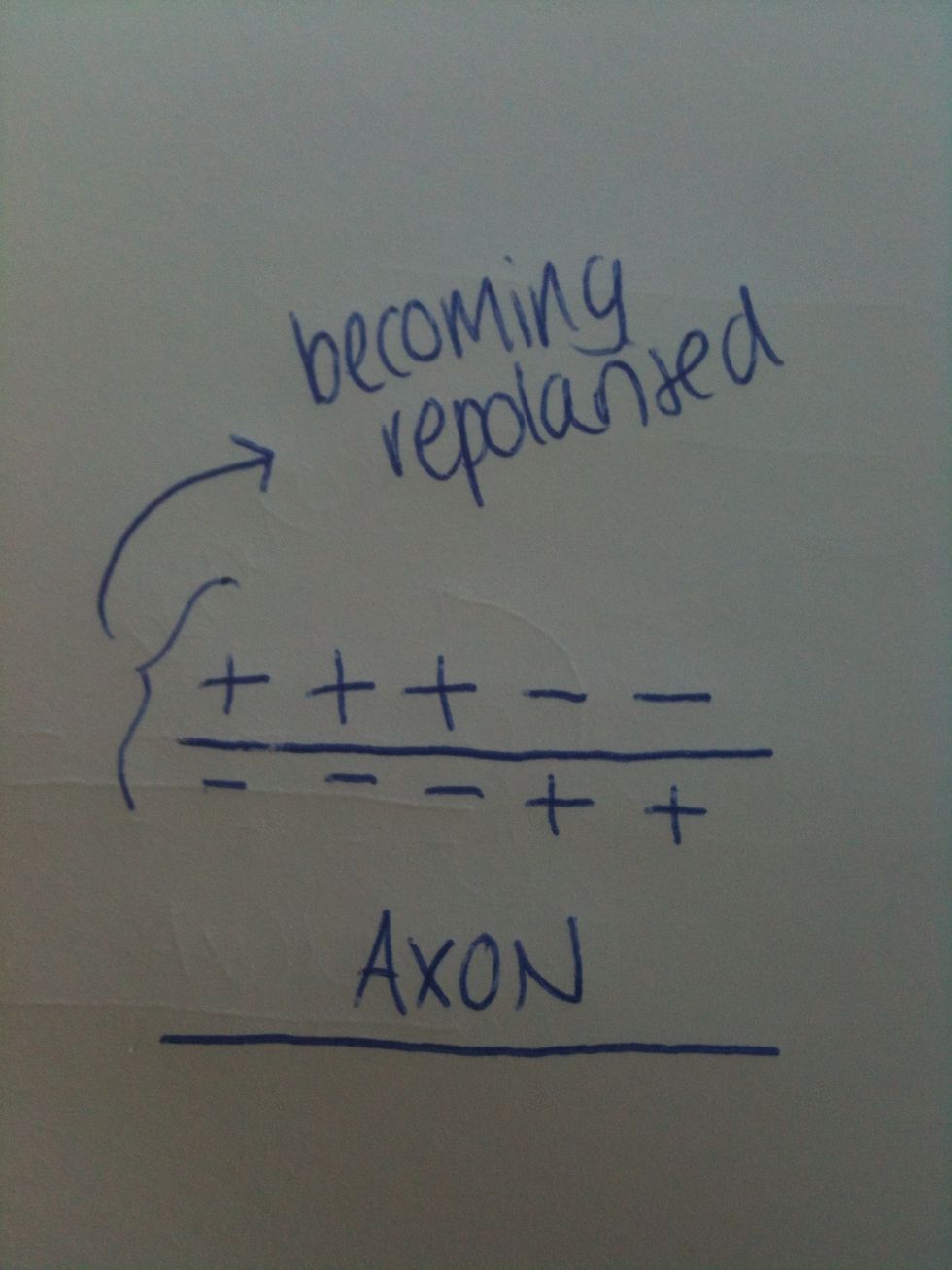
This results in the membrane becoming polarised again.
- 1.0 Axon Membrane
- 1.0 Sodium-potassium Pump
- 1.0bnch K+ Protein Channels
- 1.0bnch Na+ Protein Channels
- 1.0bnch Na+ Ions
- 1.0bnch K+ Ions
The Conversation (0)
Sign Up