How to classify plants
Plants can be classified into 5 main groups based on their leaves, stem, roots and methods of reproductive. This guide will teach you about the five main categories of plants and their features.
652
STEPS
TOOLS
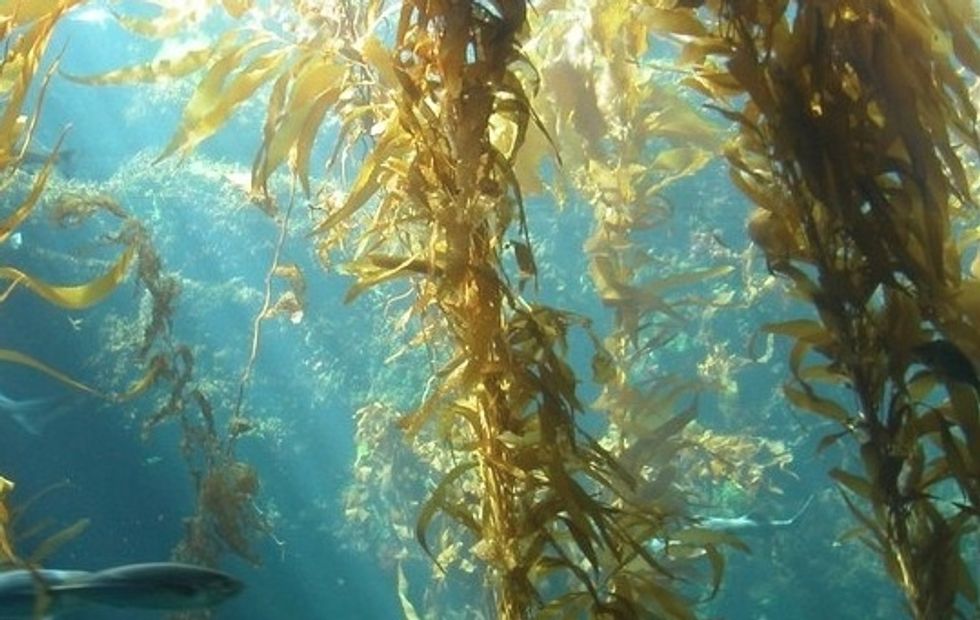

ALGAE
ALGAE are a diverse group of plants that include seaweed to microscopic diatoms. They do not have leaves, roots or stems like land plants but can make their own food from sunlight by photosynthesis
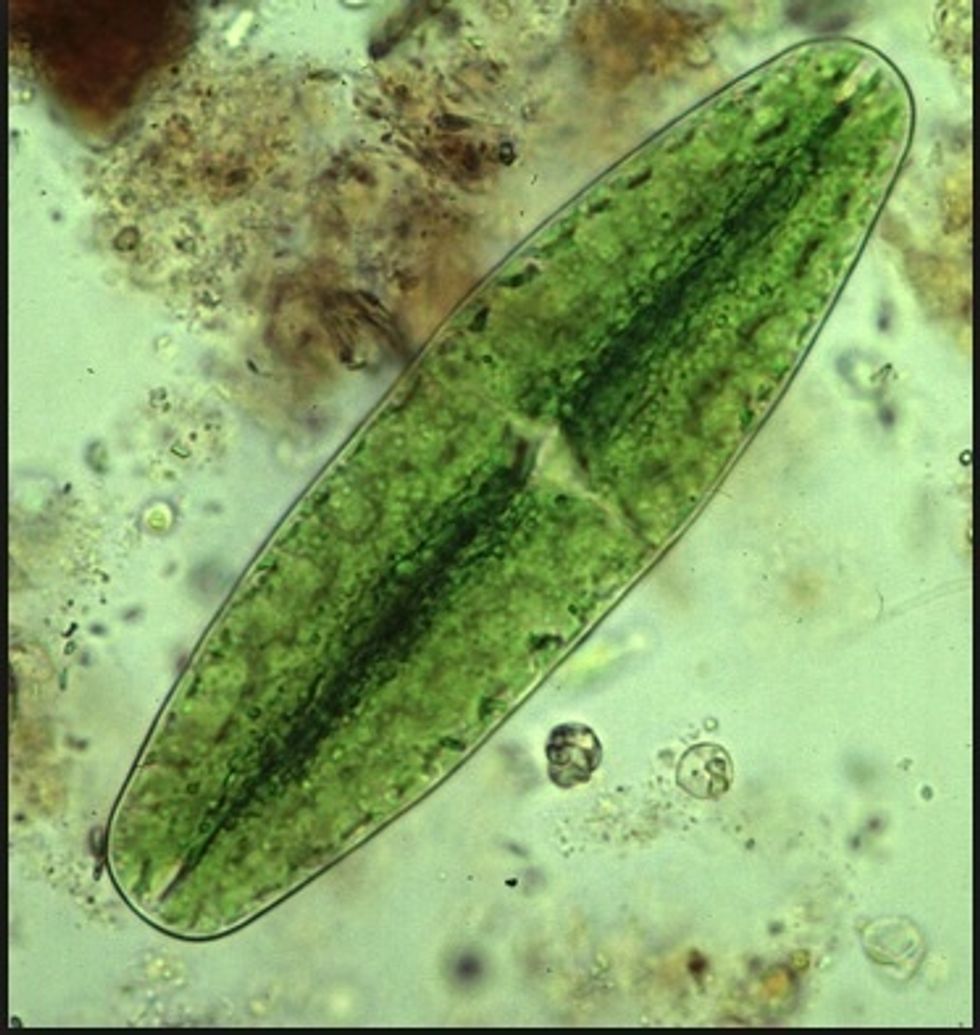
Diatoms are microscopic plant food for aquatic animals

Algae can attach itself to the sea floor or rocks with something called a 'holdfast'
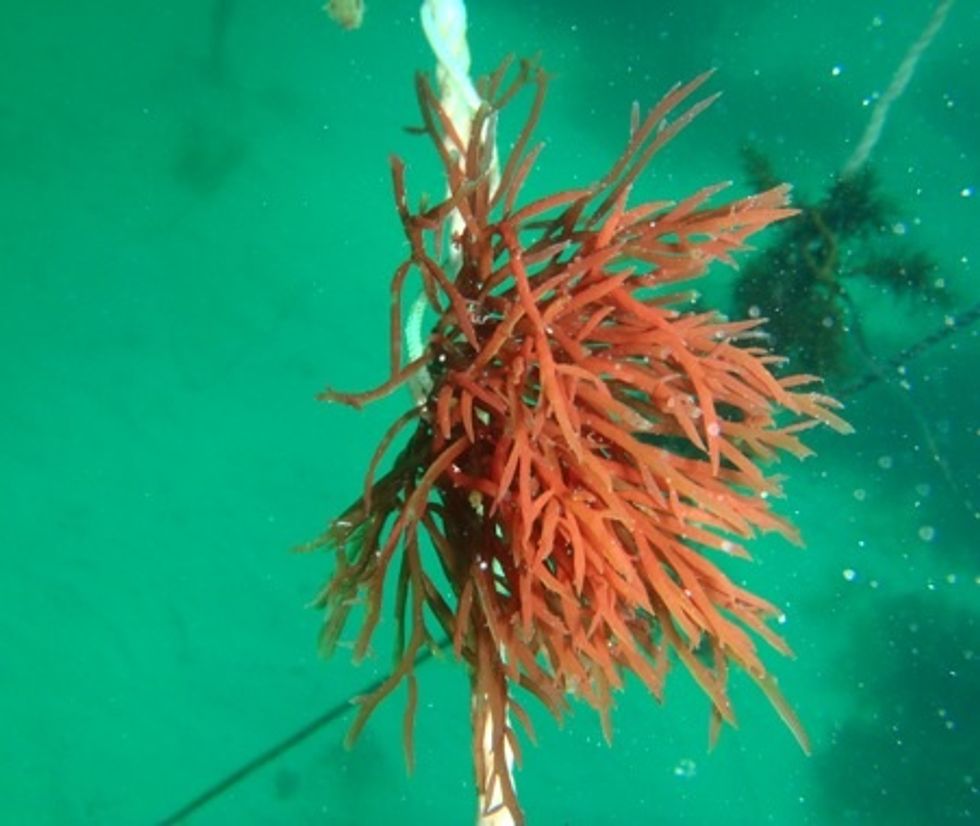

Seaweed can come in a variety of colours and are the largest of the algae group
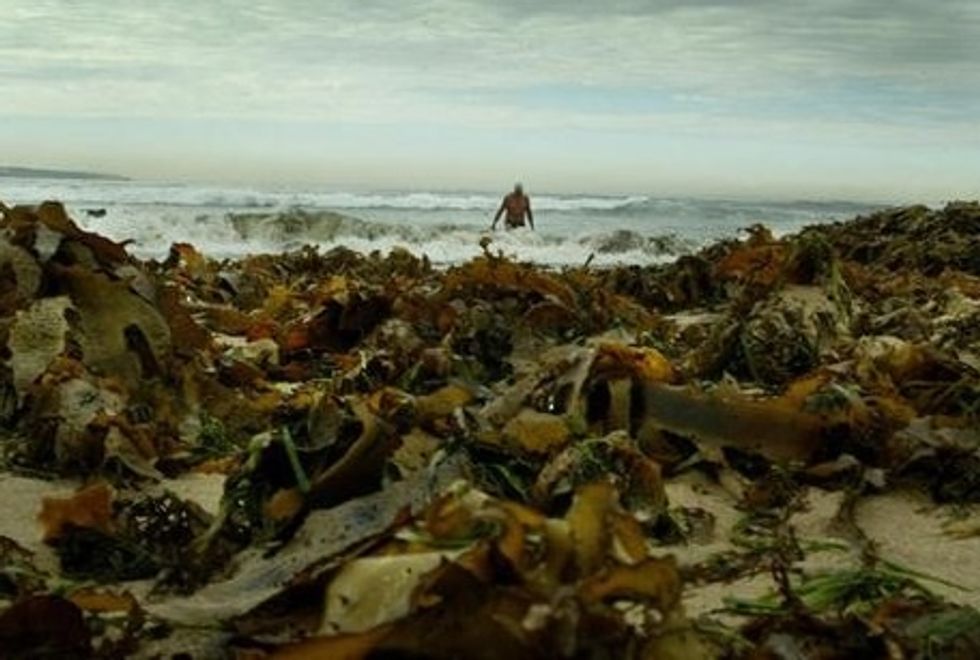

Brown kelp washed up onto a beach
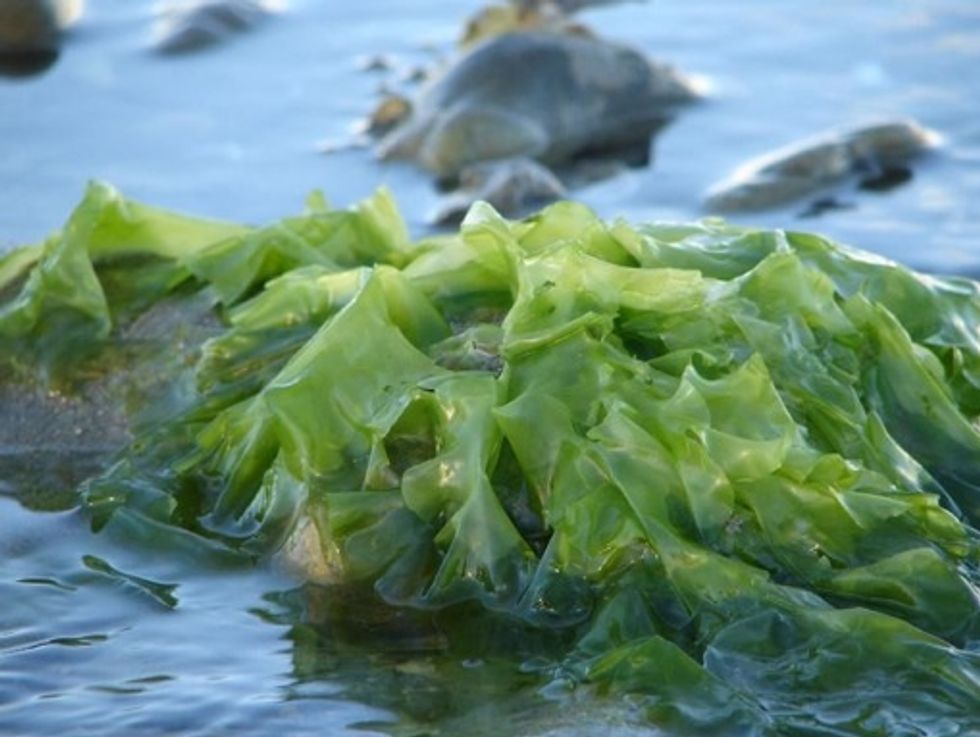

Because hey have no true stem or roots - algae need to live in water to keep them alive
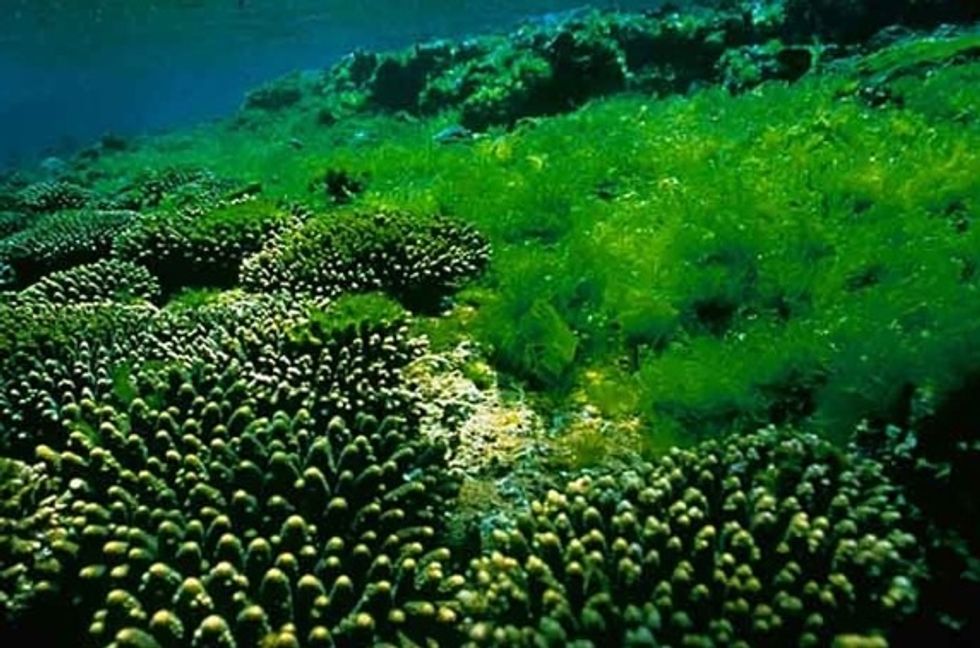

We call plants that live in water like algae 'aquatic plants'
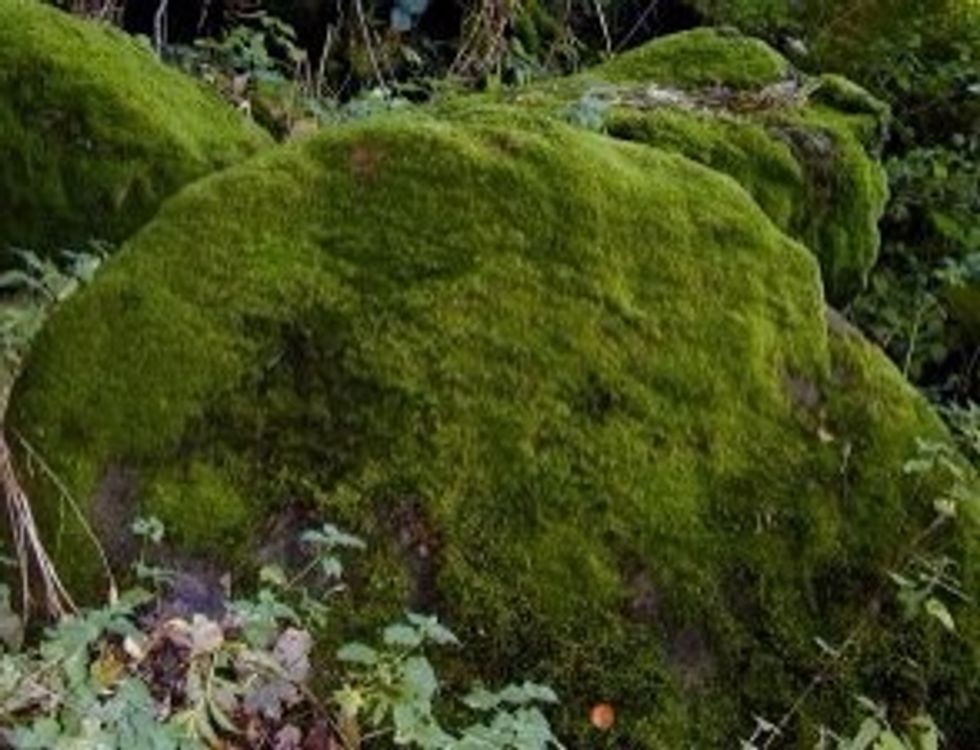

MOSSES & LIVERWORTS
MOSSES & LIVERWORTS are little plants. They don't have true stems or a vascular system like other land plants so they cannot transport nutrients over a long distance and they don't grow very tall.
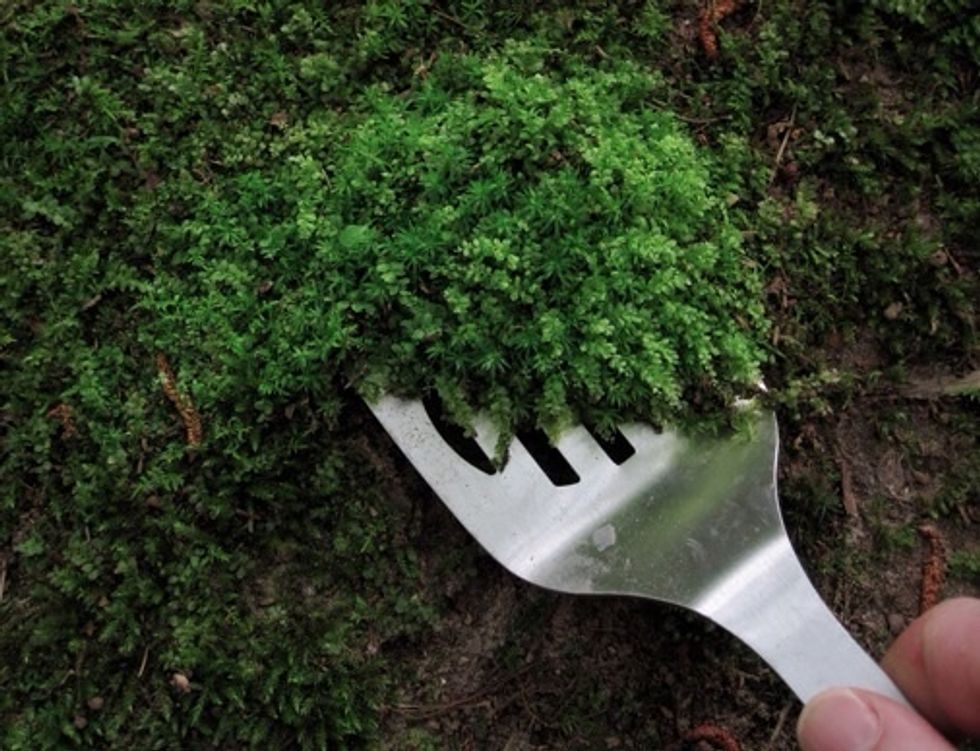

Mosses form a dense carpet of miniature looking clusters of leaves
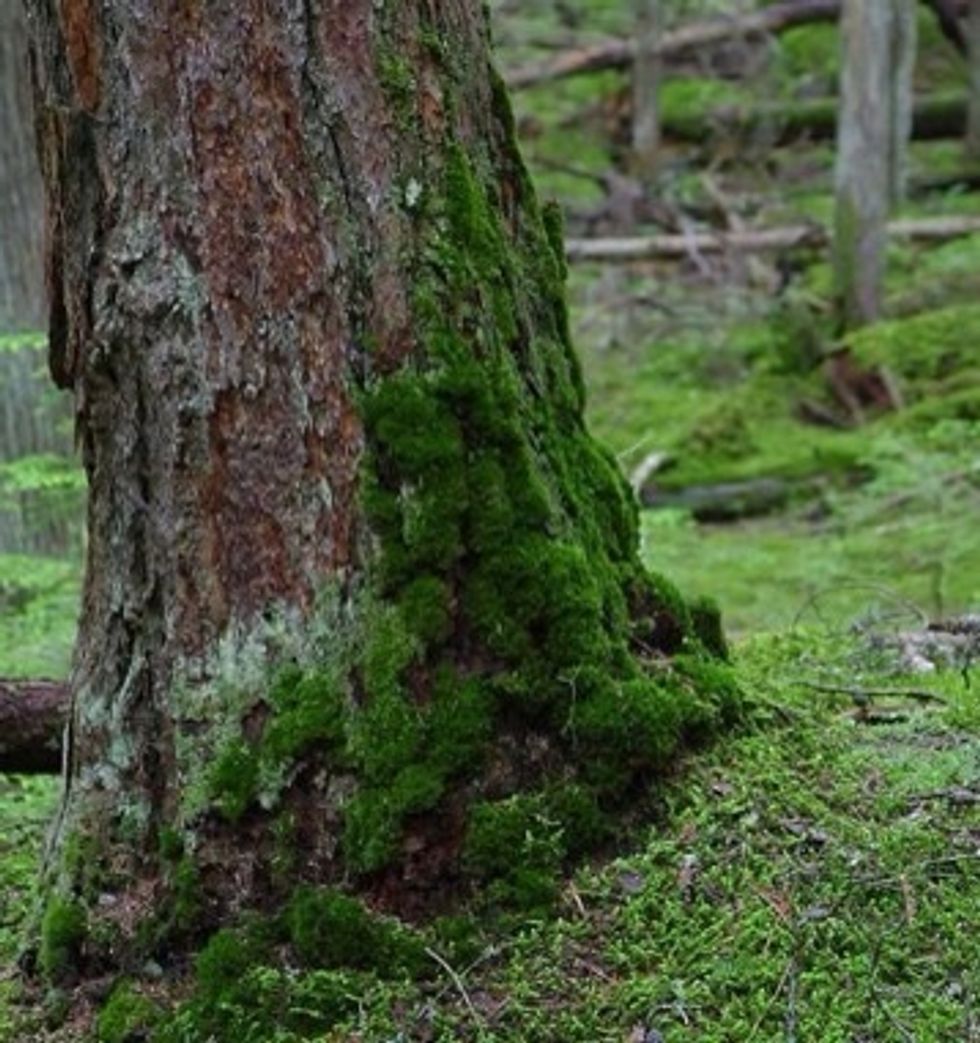

Moss can grow on the ground,rocky areas and even in tree bark
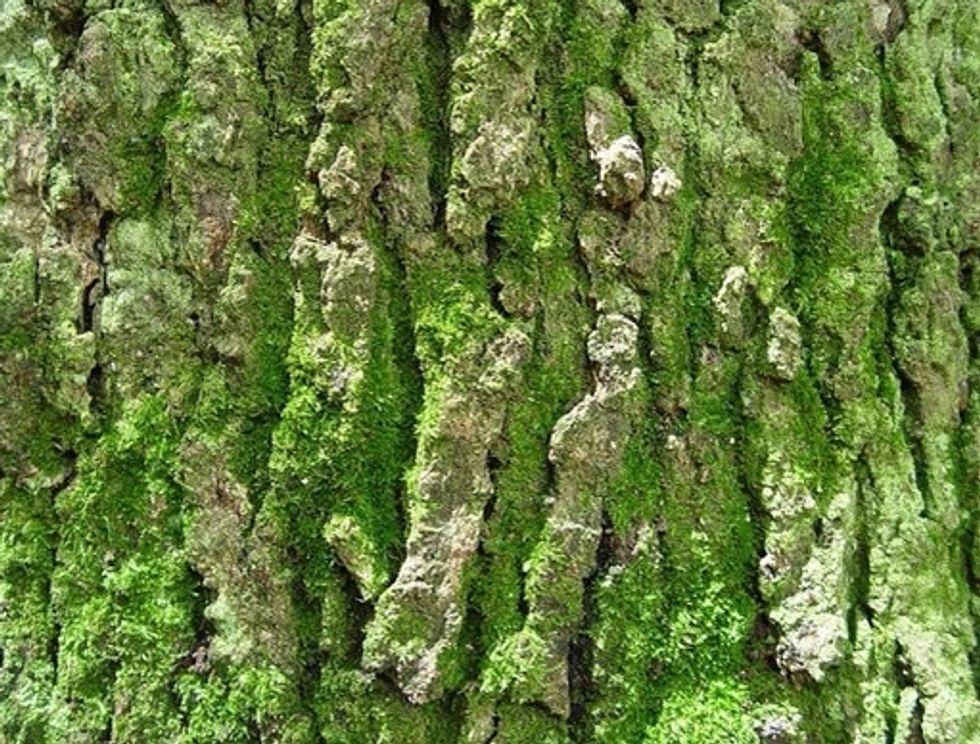

Mosses don't have true roots either but have hair-like parts called rhizoids. Mosses and liverworts also rely on water to help them reproduce with spores.
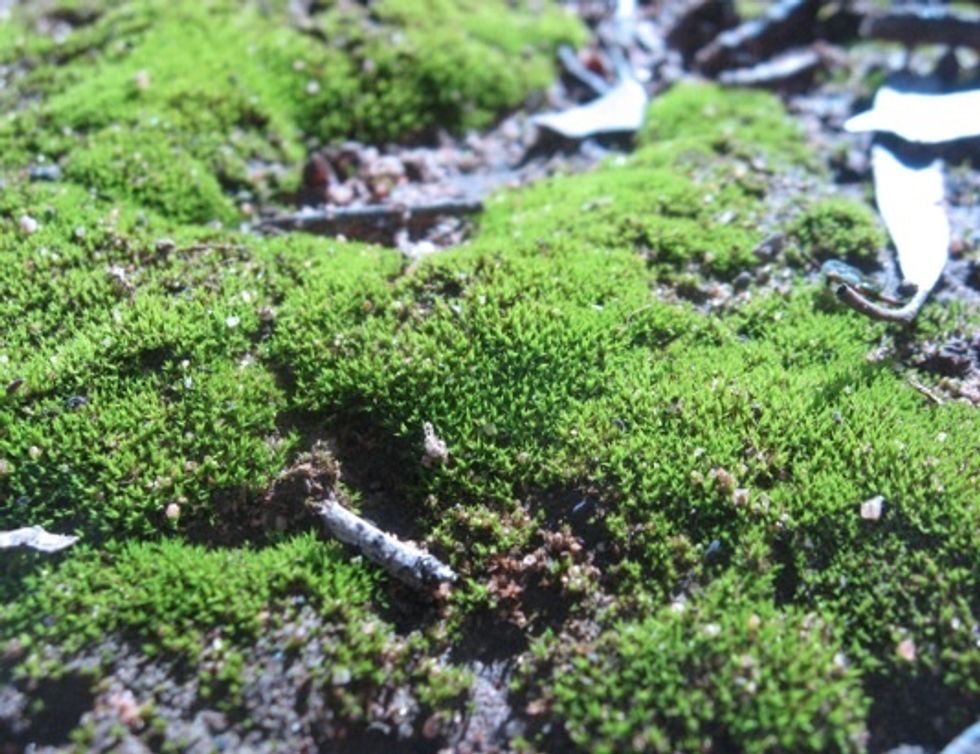

With no vascular tissue and spores for reproduction, mosses thrive in moist areas
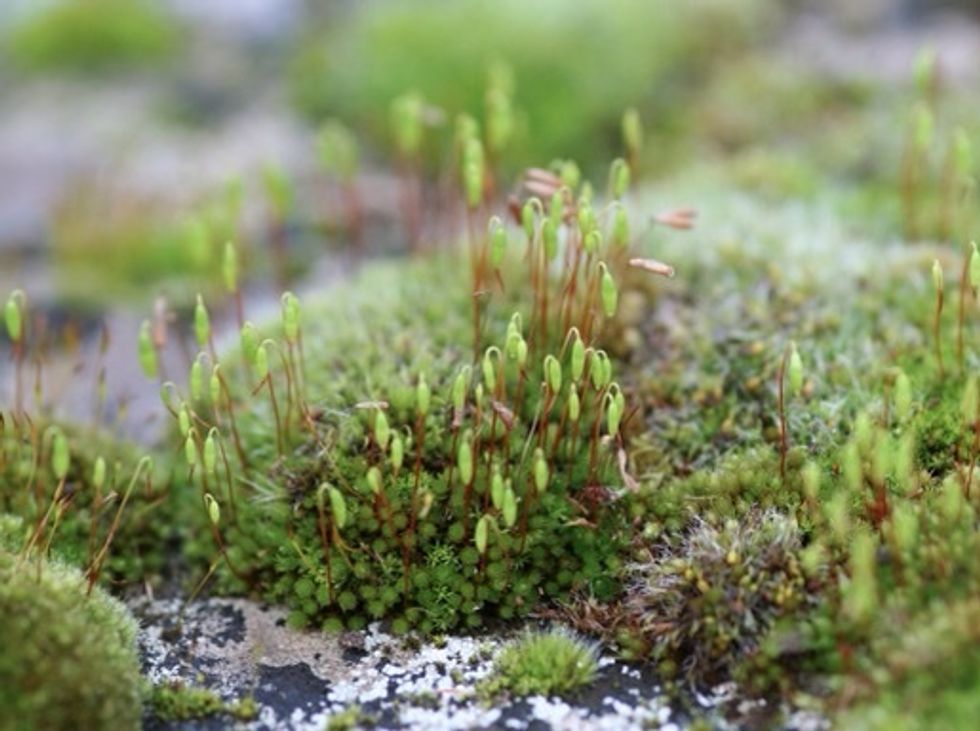

These are liverwort spore pods. Liverworts grow a little higher than mosses

FERNS
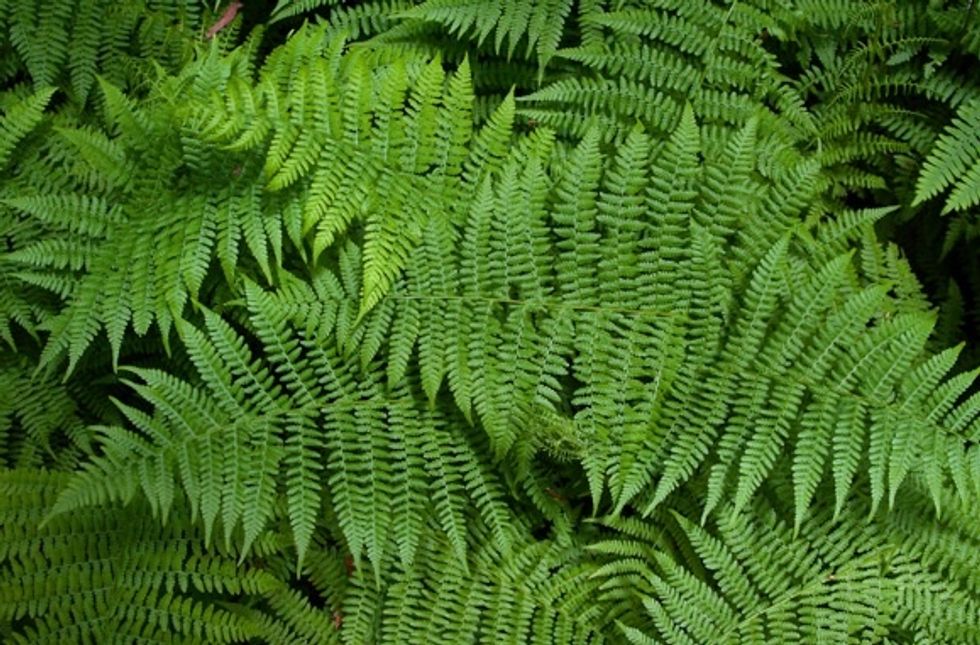
FERNS are shade loving plants. They have feather-like leaves called 'fronds'. They have true stems and roots that can be anchored in soil or to a tree trunk. They are generally short.

These are the typical feather-like 'fronds' of a fern
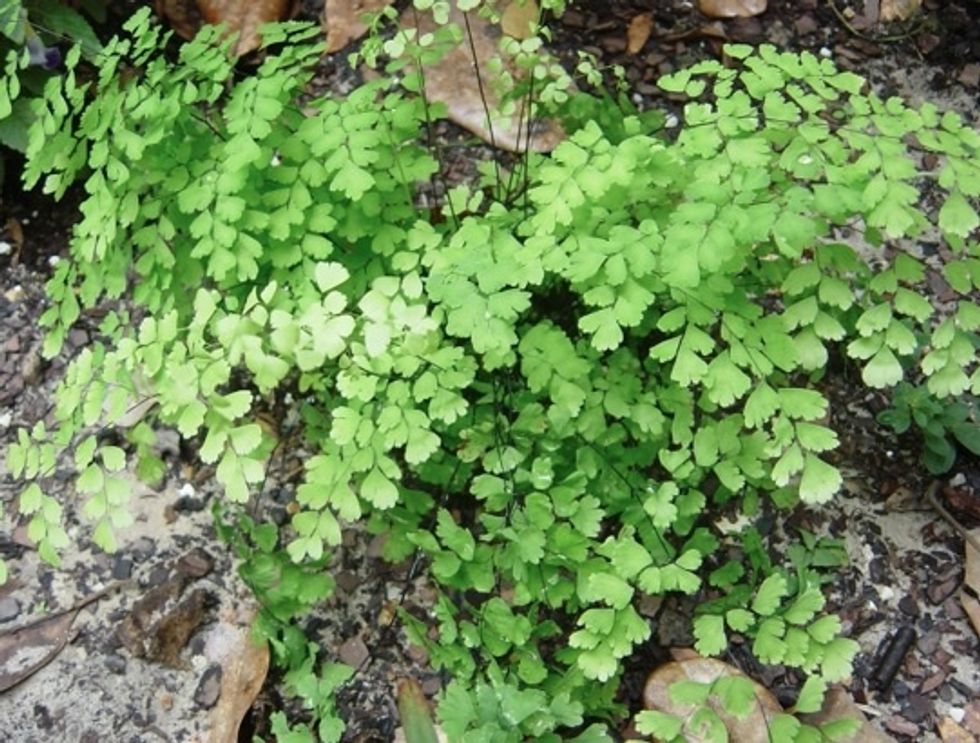

Fern fronds can also be delicate and round like this 'maiden hair fern'
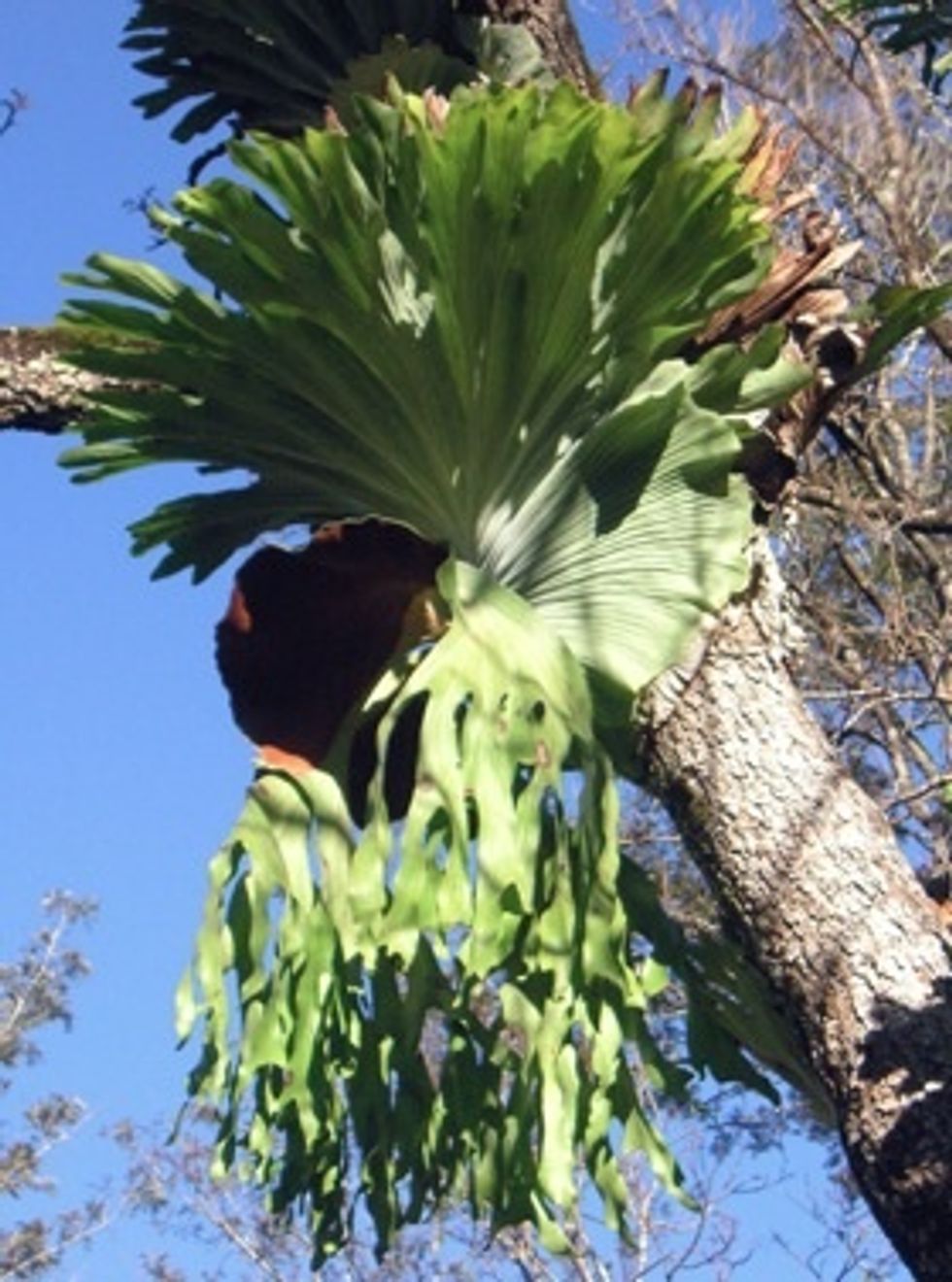

Ferns can grow in trees as well as soil
Ferns reproduce by spores on the underside of their 'frond'. These spores need water so ferns often live in damp, shady areas.
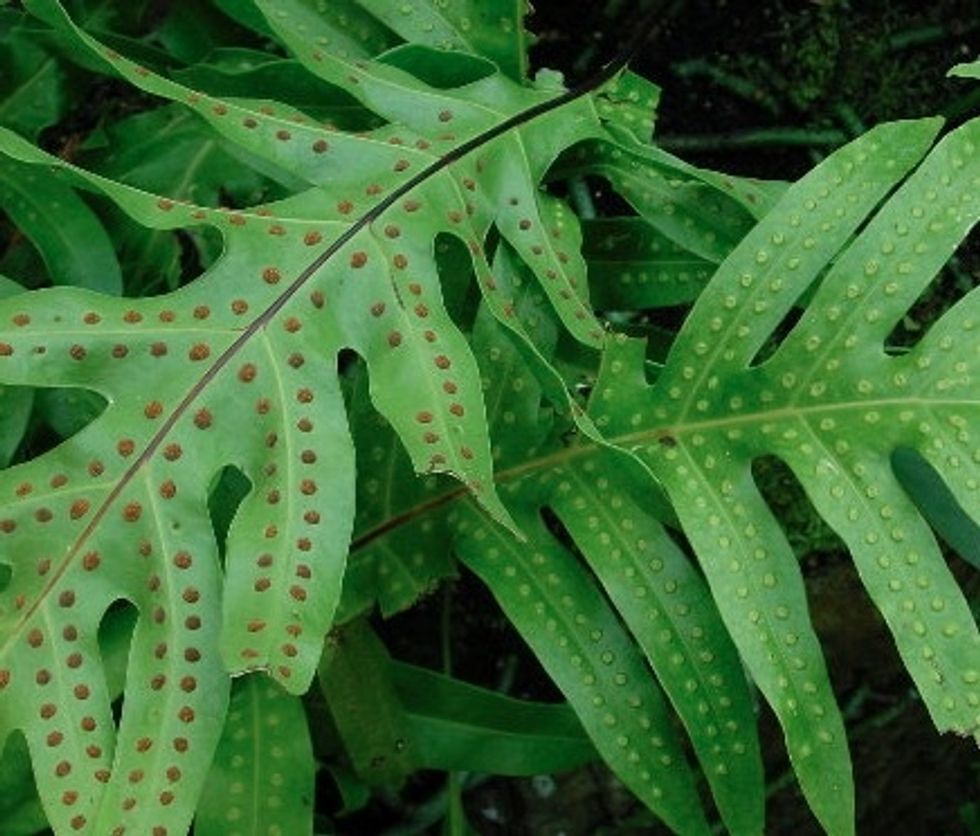

Spores on the underside of a fern frond
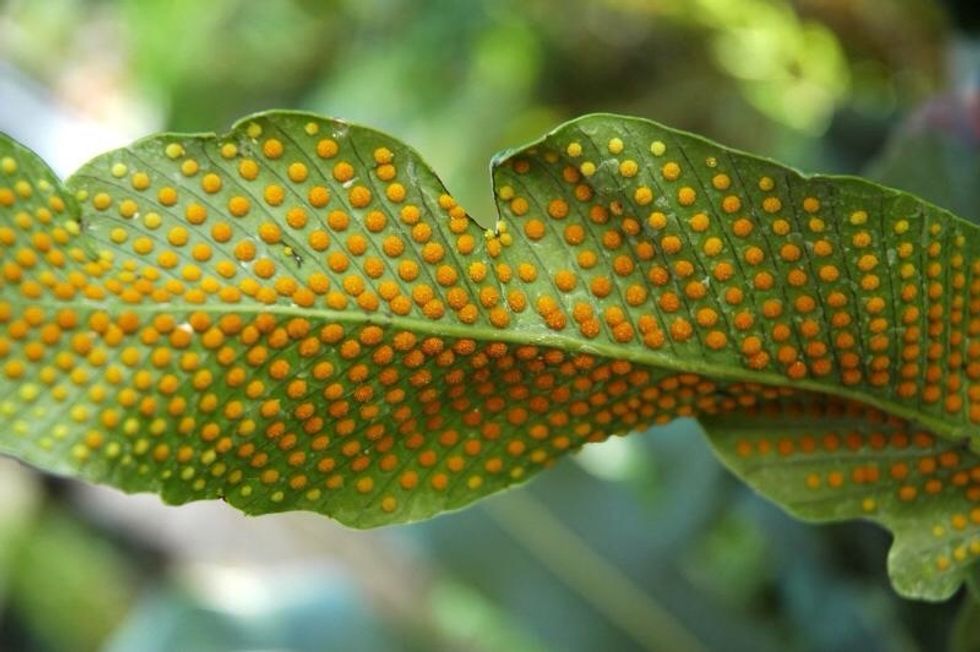
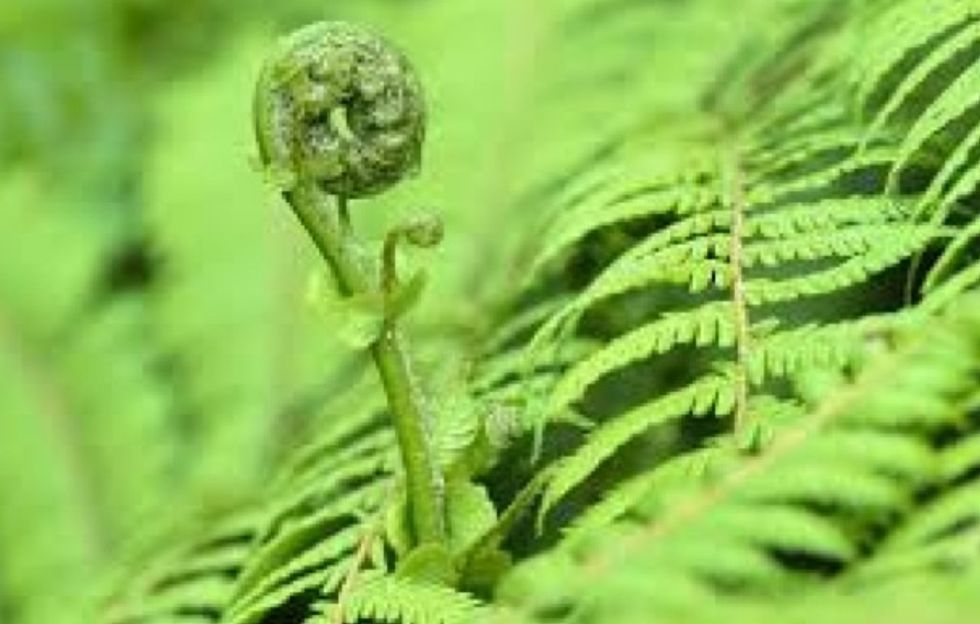


The spores germinate and grow into a 'sporophyte' that uncurls to form a new fern plant.
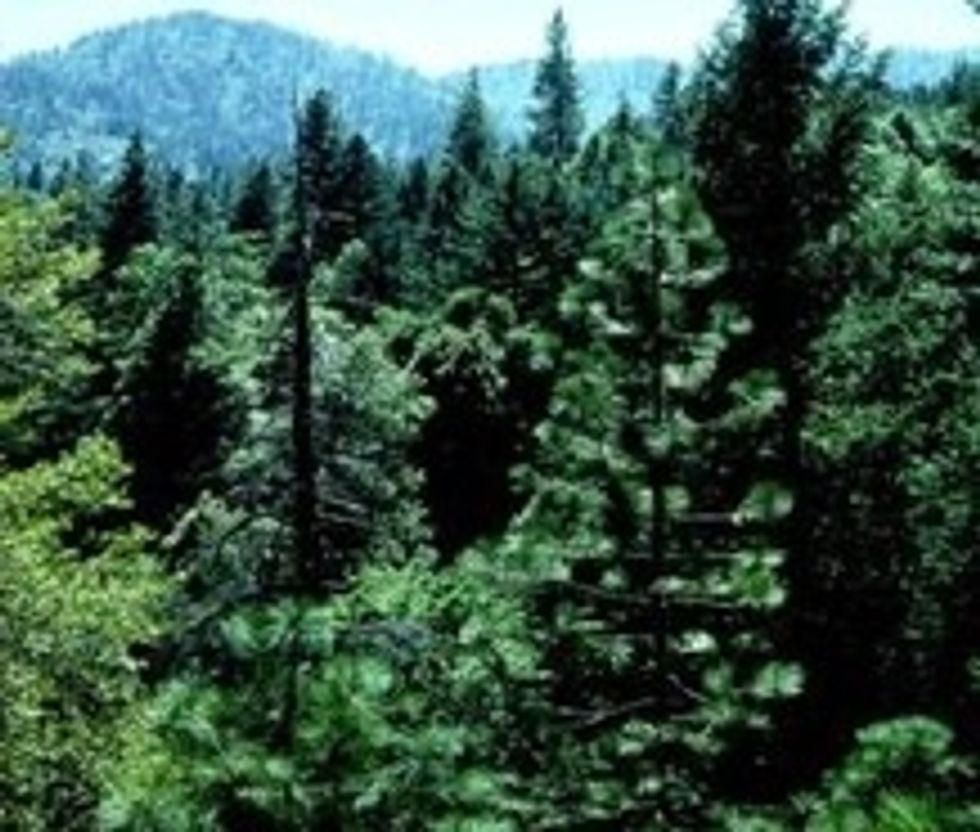

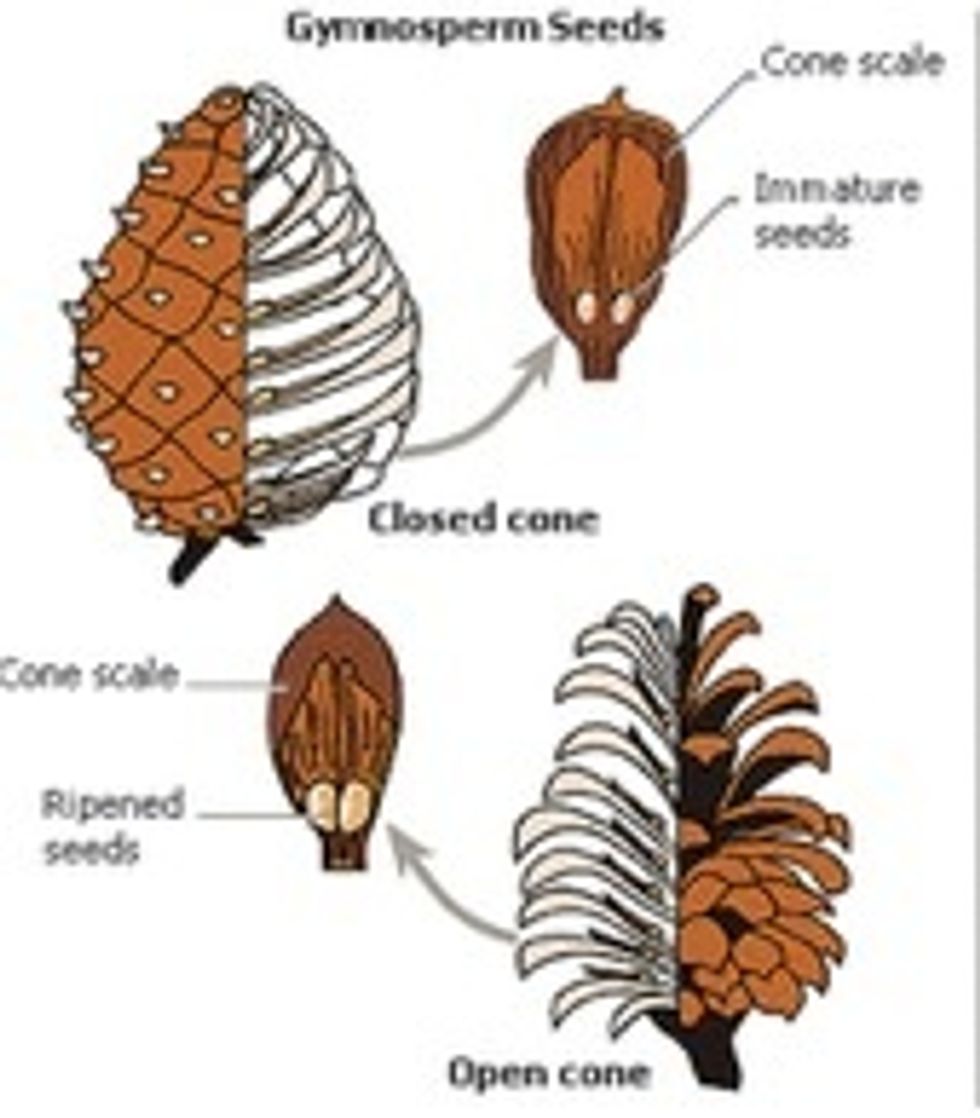
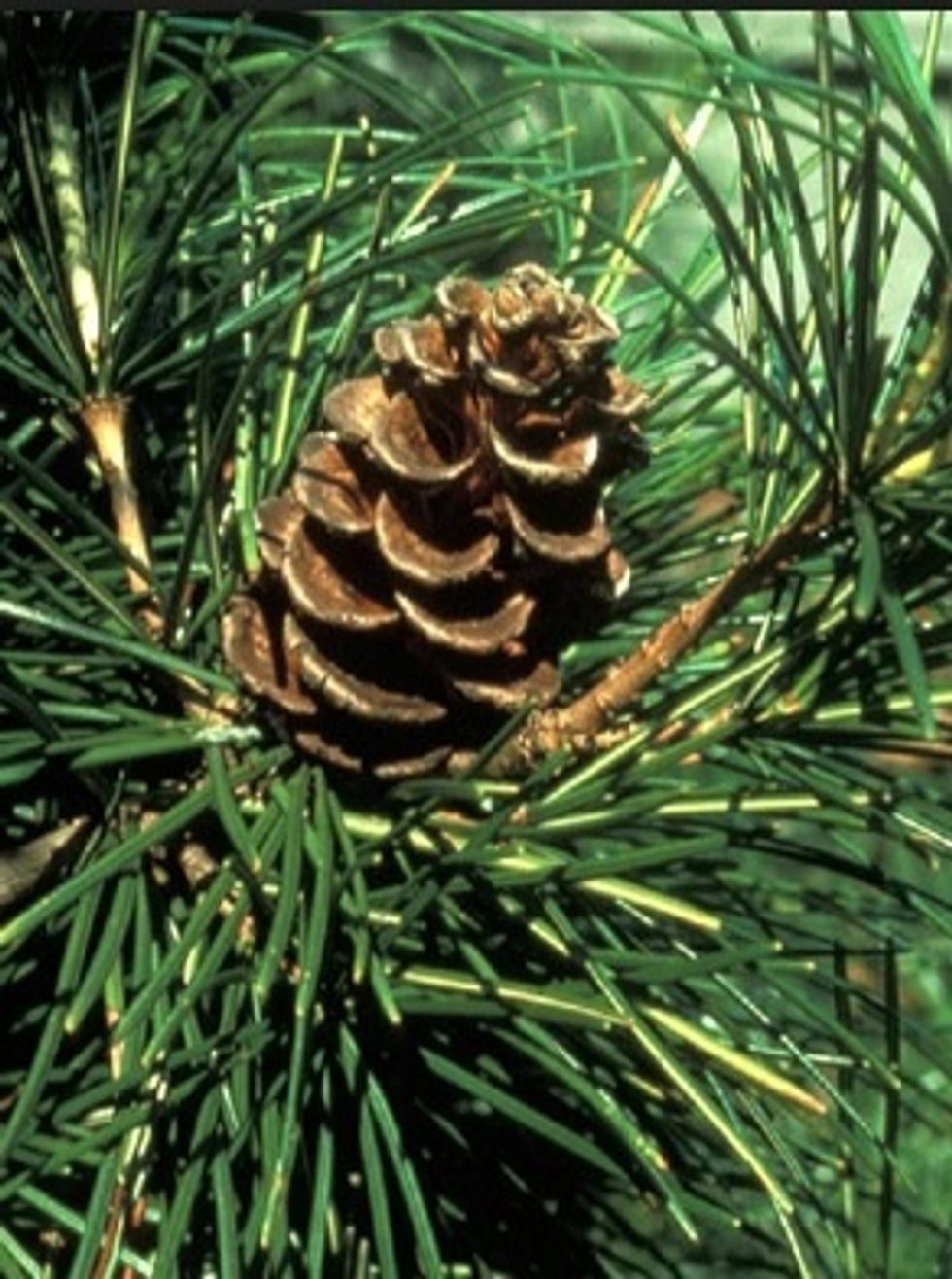
CONIFERS ( also called Gymnosperm)
CONIFER is a Latin word, made up of two words, conus (cone) and ferre (to bear). So conifers are plants that use woody cones to reproduce.
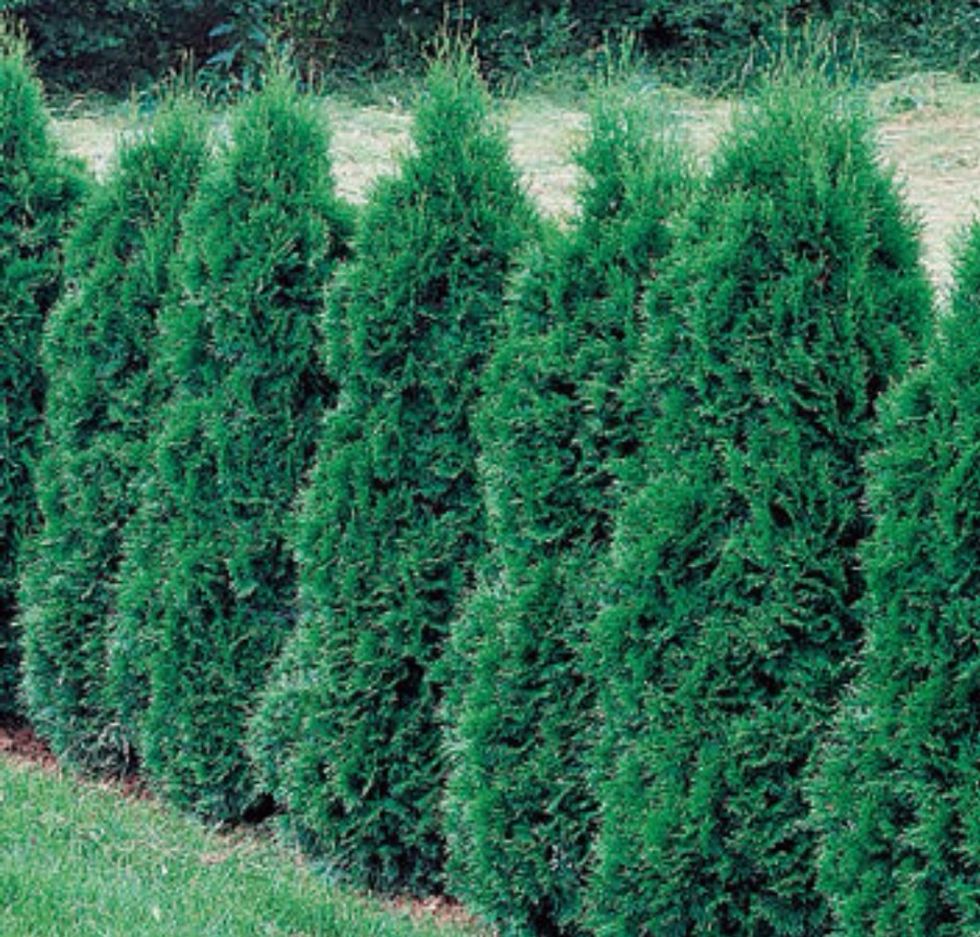


The classic fir Christmas tree is a conifer.Most conifers are trees that grow quite tall, only a few are shrubs.
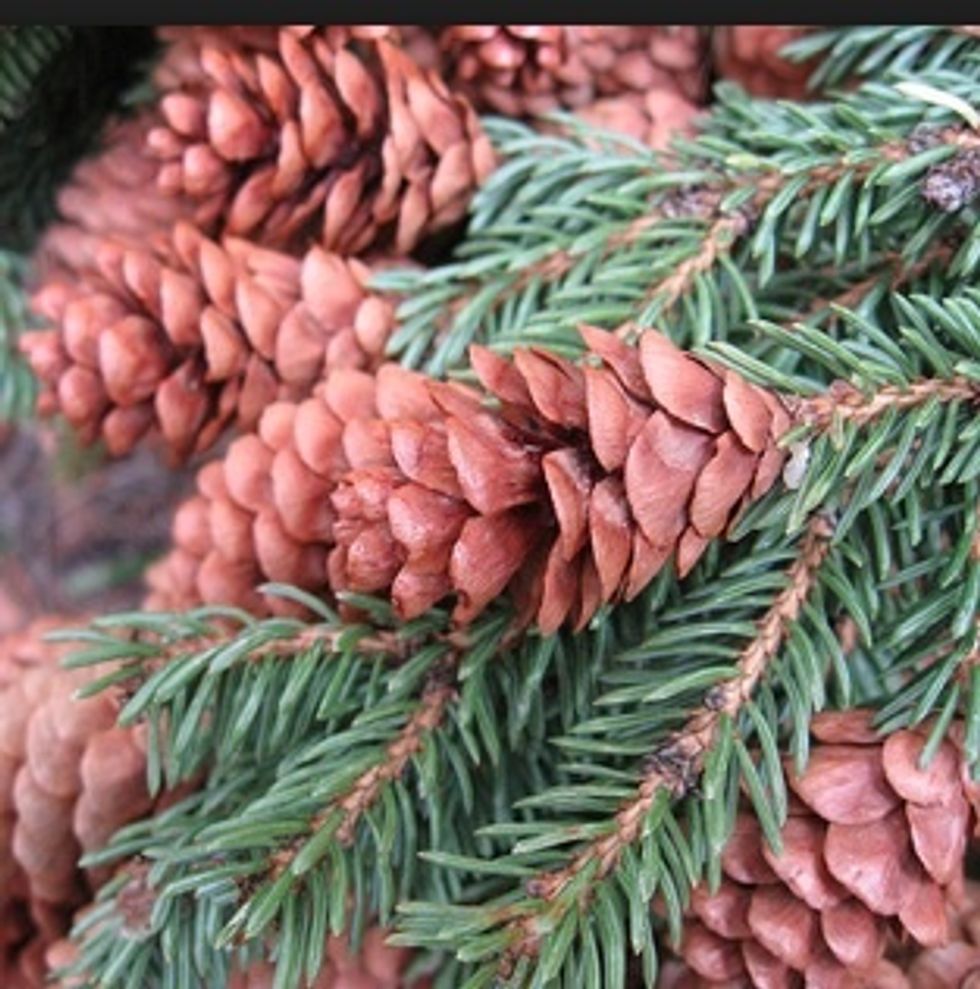
Conifers keep their seeds hidden inside a cone until they are ready to be released. Then the cone drops off.

This cone is still closed with its seeds inside
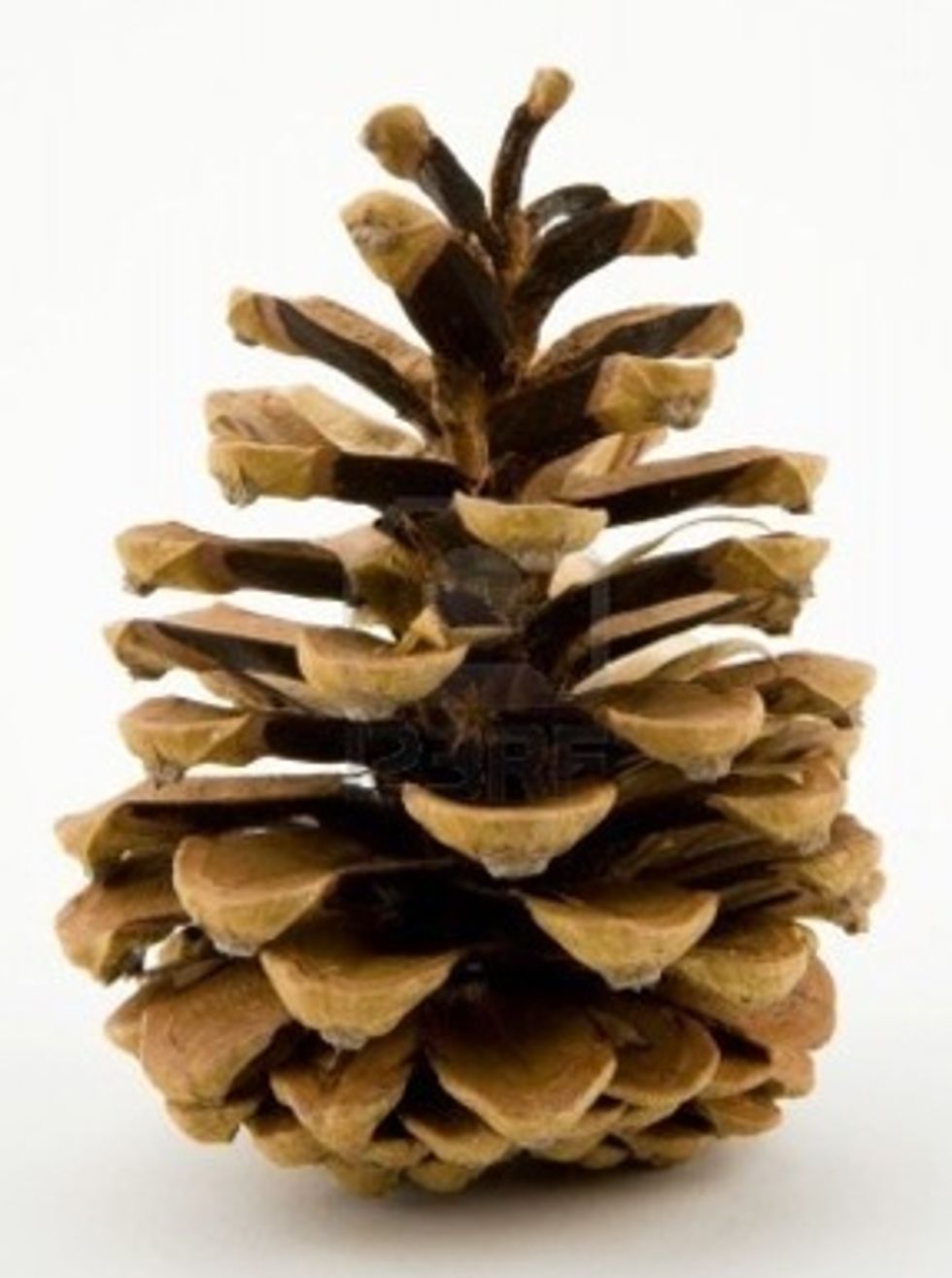

This cone has released its seeds and has fallen from the branch to the ground.
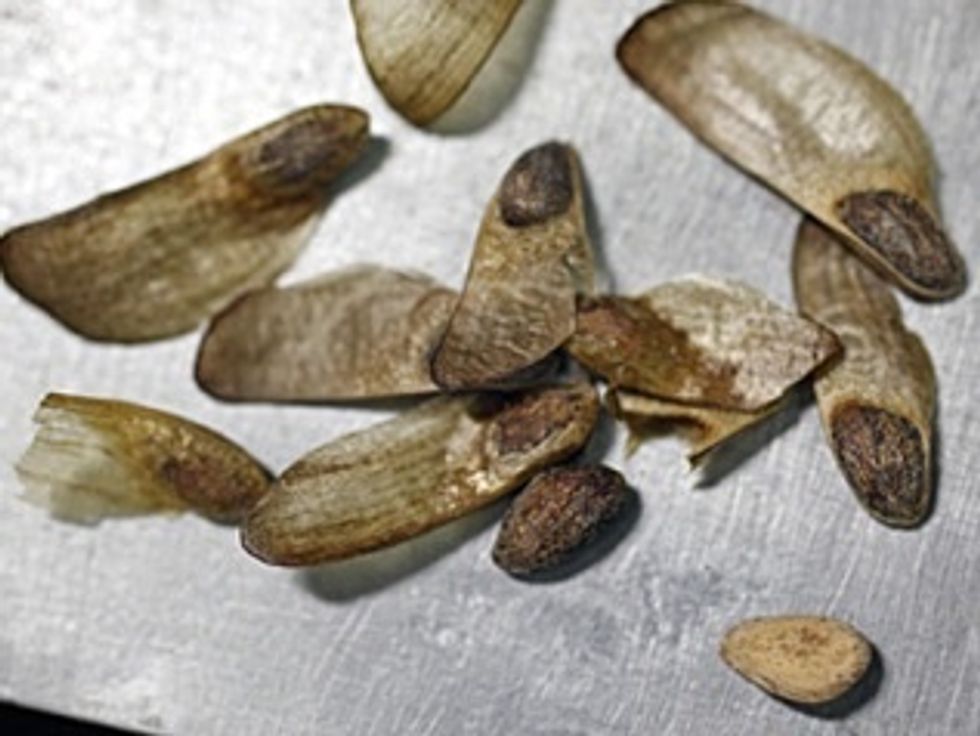

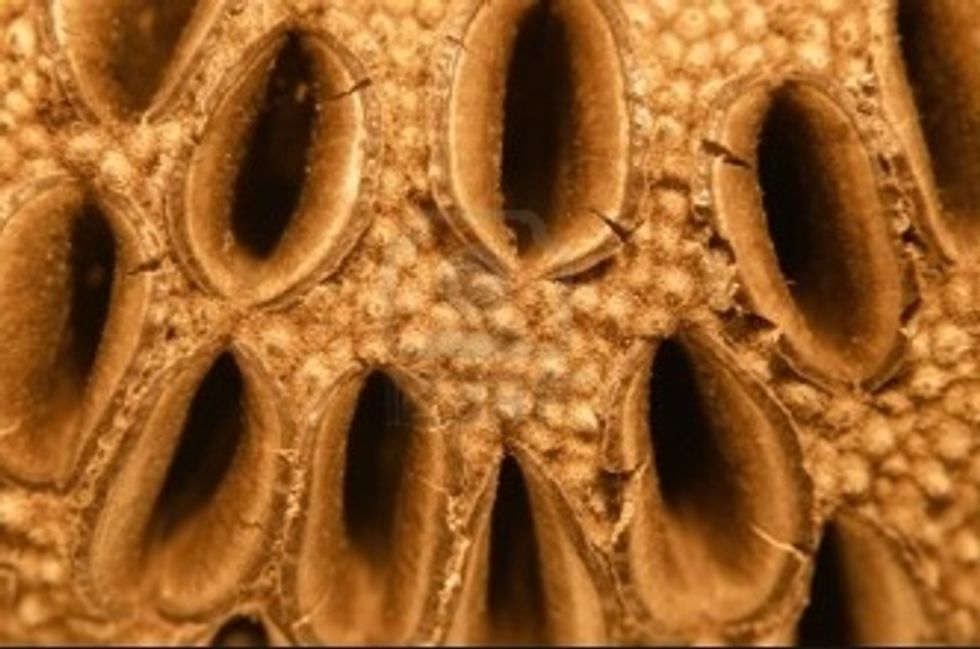
Winged seeds from inside a cone - when they are released they fly a little like a helicopter to the ground
Conifers also have leaves but they are 'needle-like' or 'fir-like' in shape. They have proper roots and woody stems.
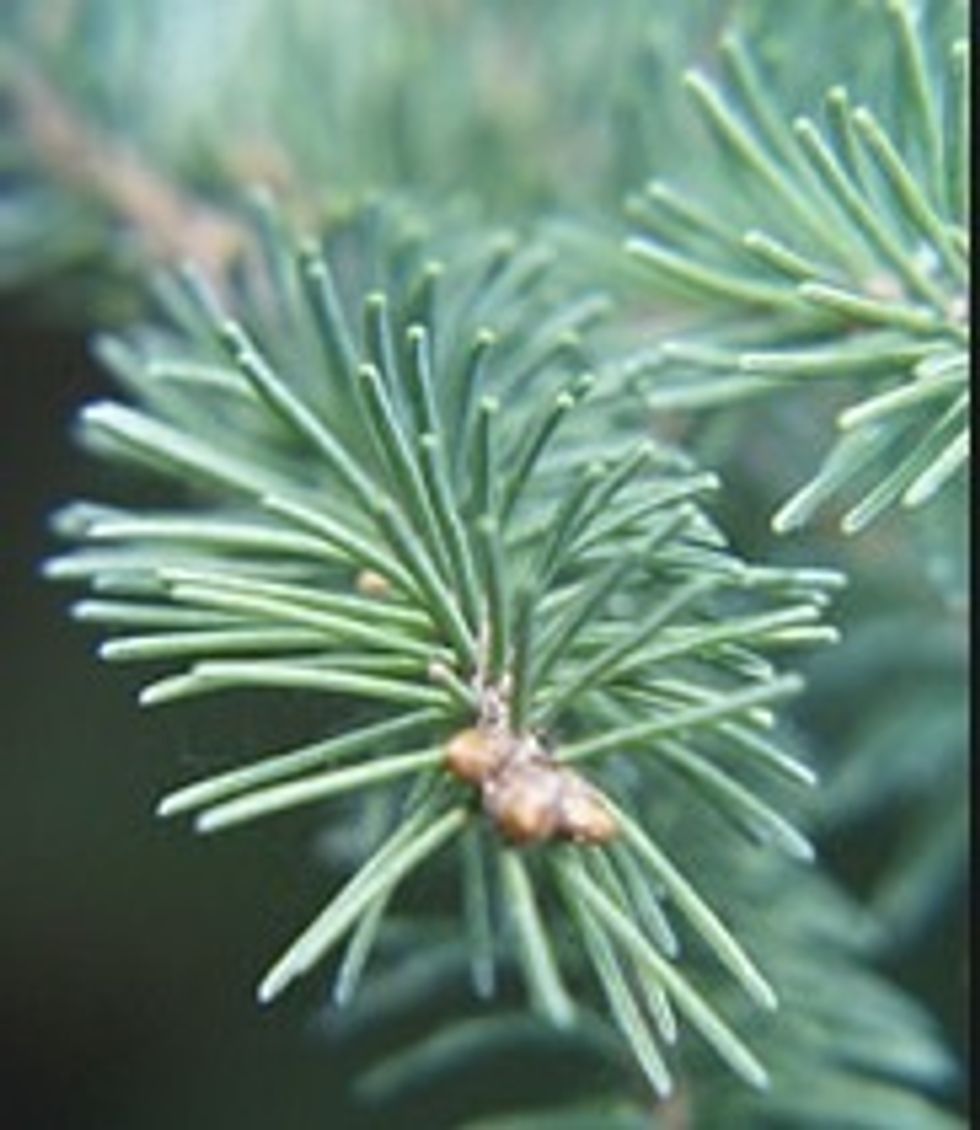

Needle-like leaves of conifers


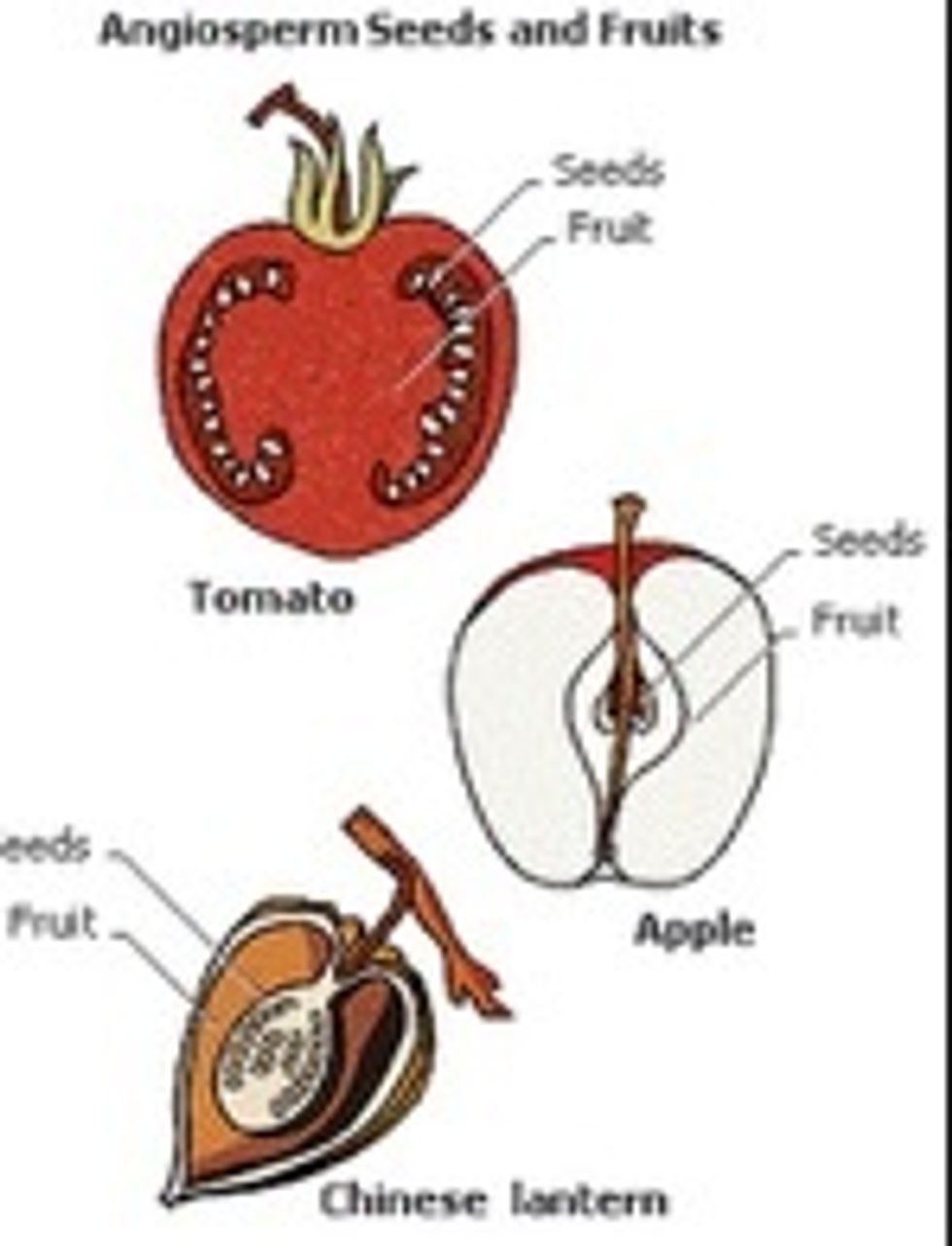
FLOWERING PLANTS ( also known as Angiosperms)
FLOWERING PLANTS are the most diverse and common type of plant. What they all have in common is that they produce flowers and fruits.
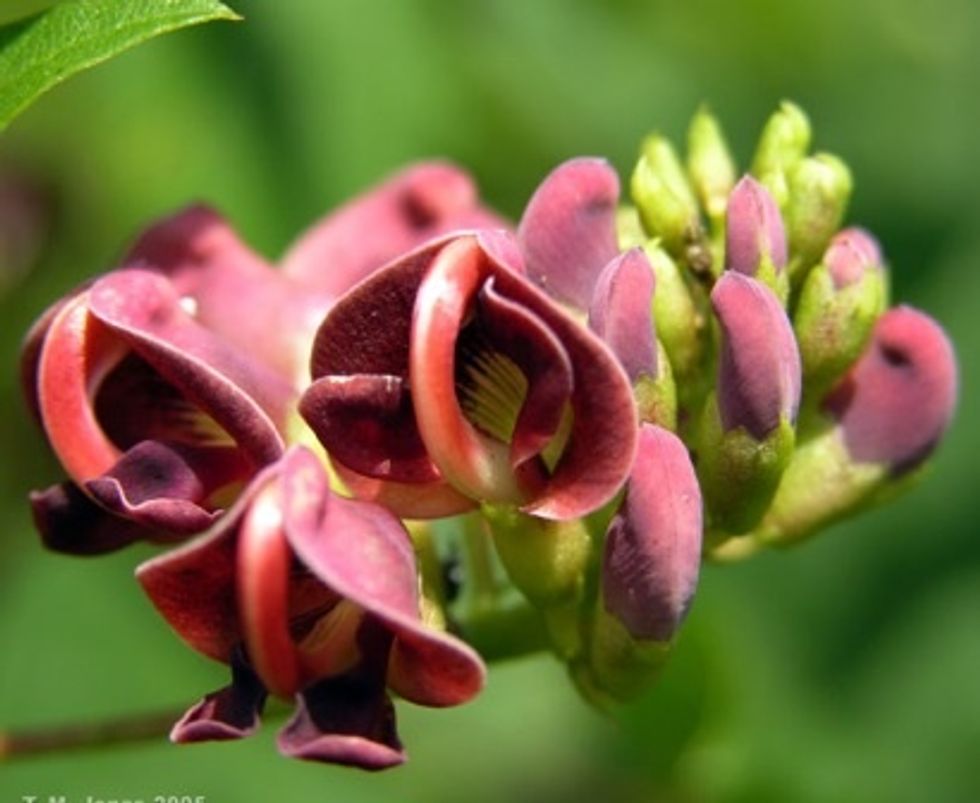
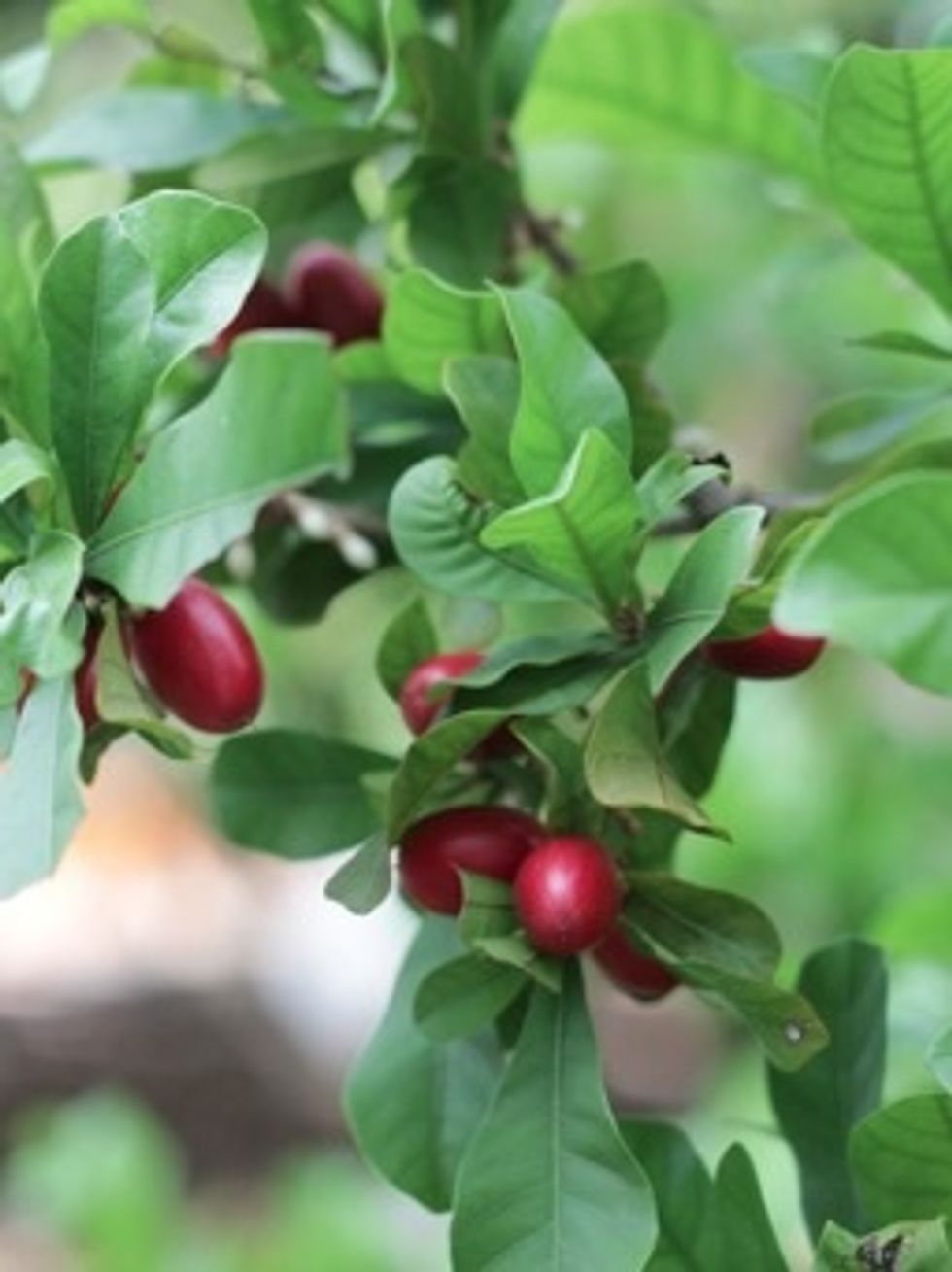
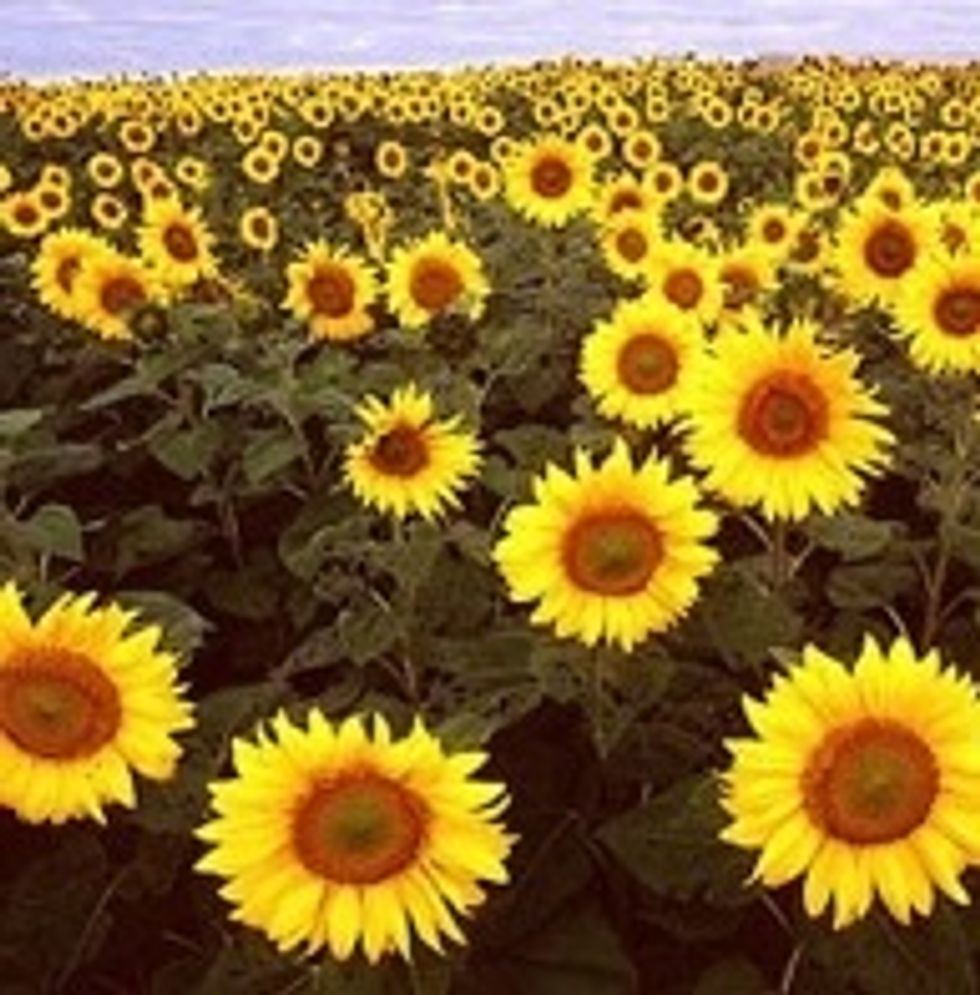



Flowering plants produce flowers with bright petals to attach insects to help them reproduce
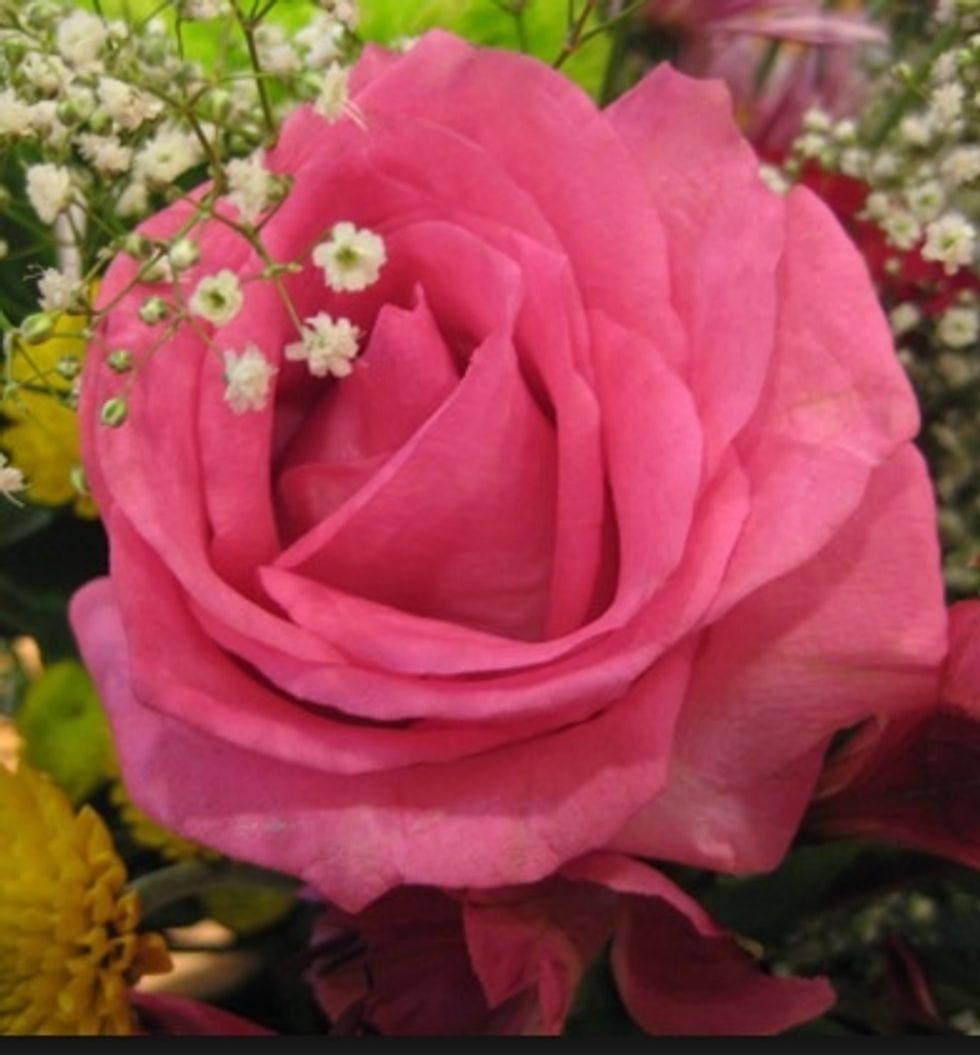

Their scent is created from sweet nectar, strategically placed at the bottom of the petals so insects will seek it out and help pollinate flowers
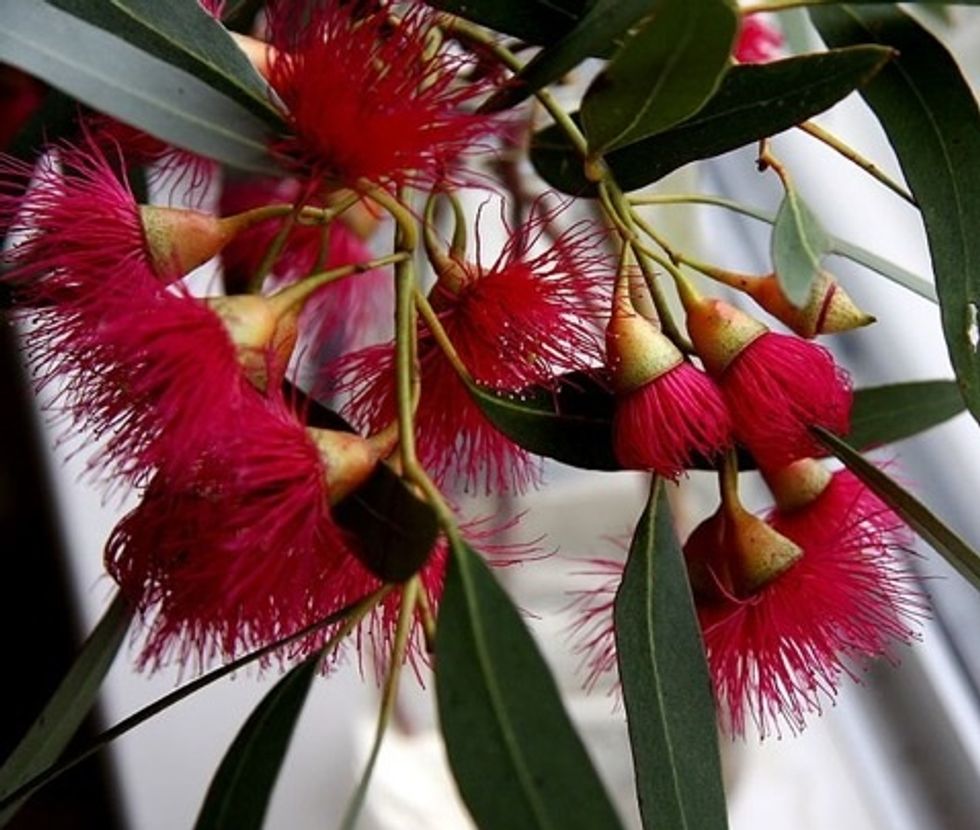

Petals can even be very thin and spiky like on Eucalyptus trees
The fruit of flowering plants usually contain seeds inside a fleshy skin covering.
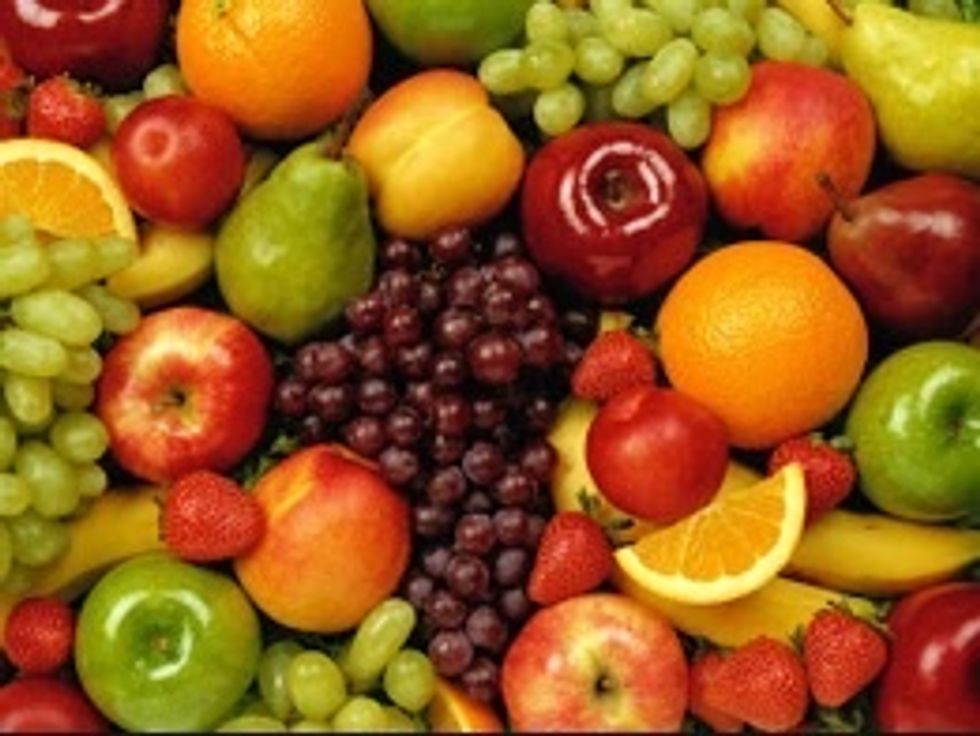

Many of the fruits we eat are from flowering plants
Flowering plants have true roots and stems so they can grow into tall trees and shrubs.
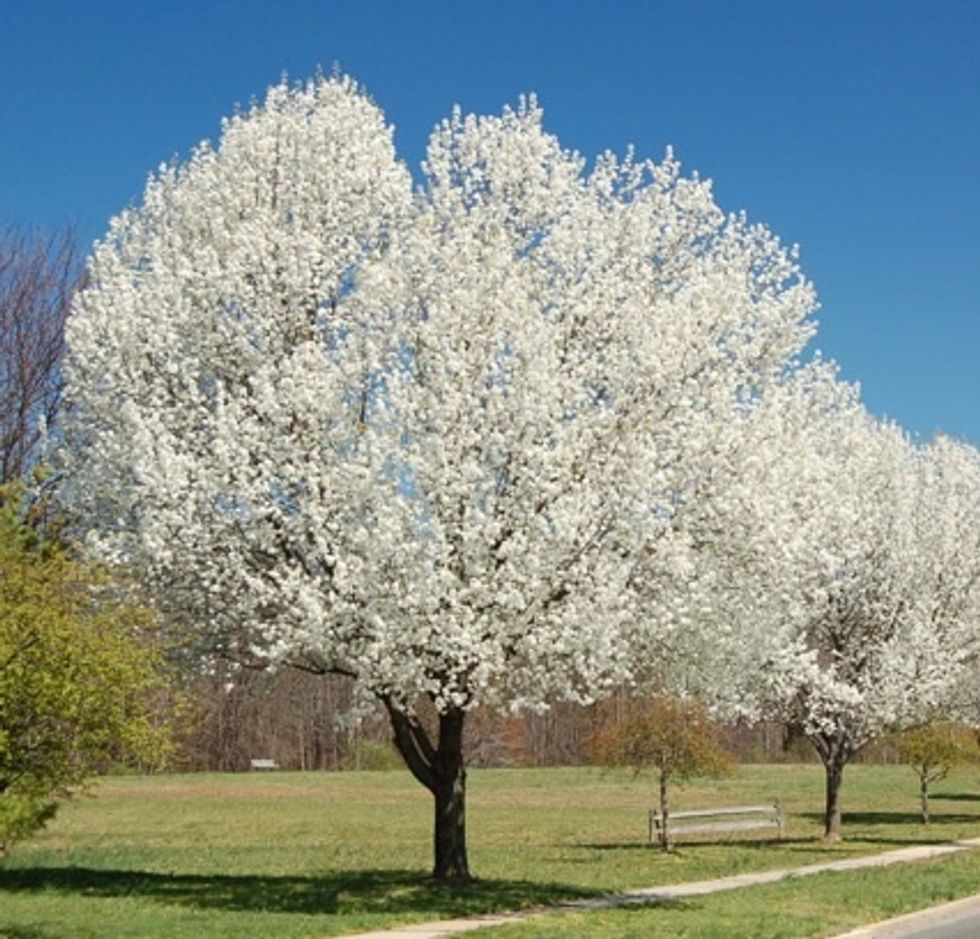
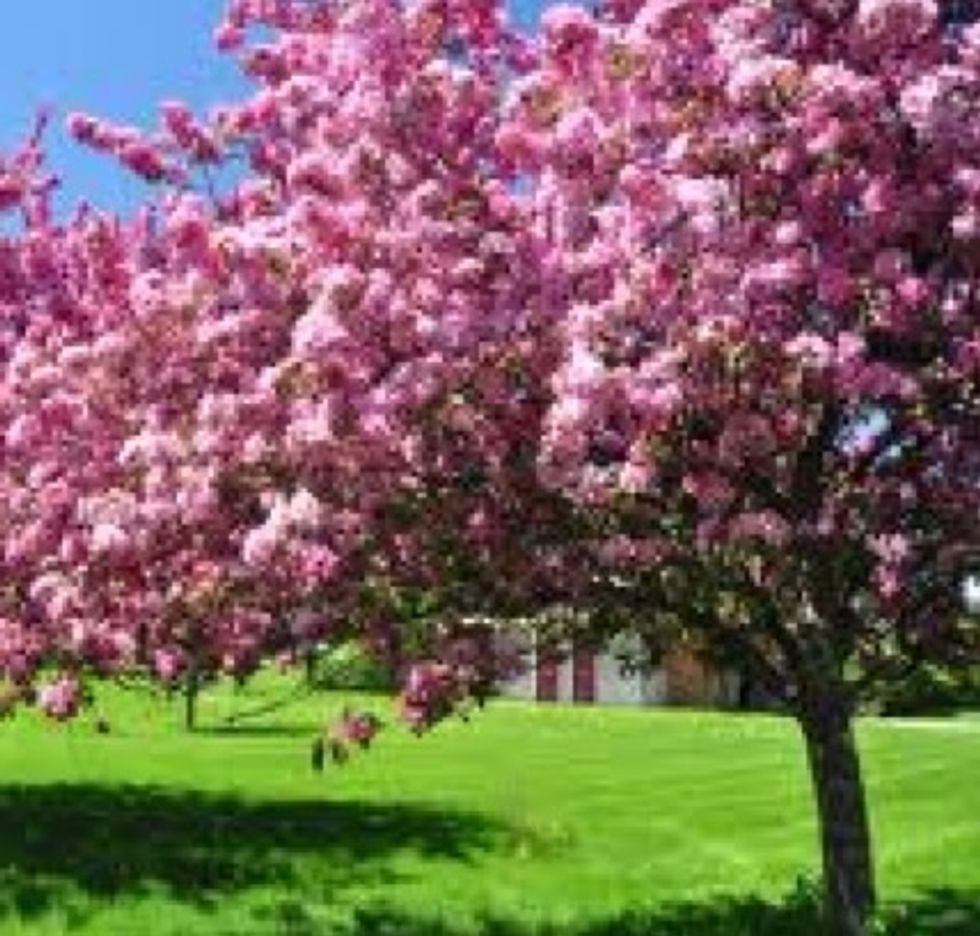


Most trees have flowers at some time during the spring and are flowering plants
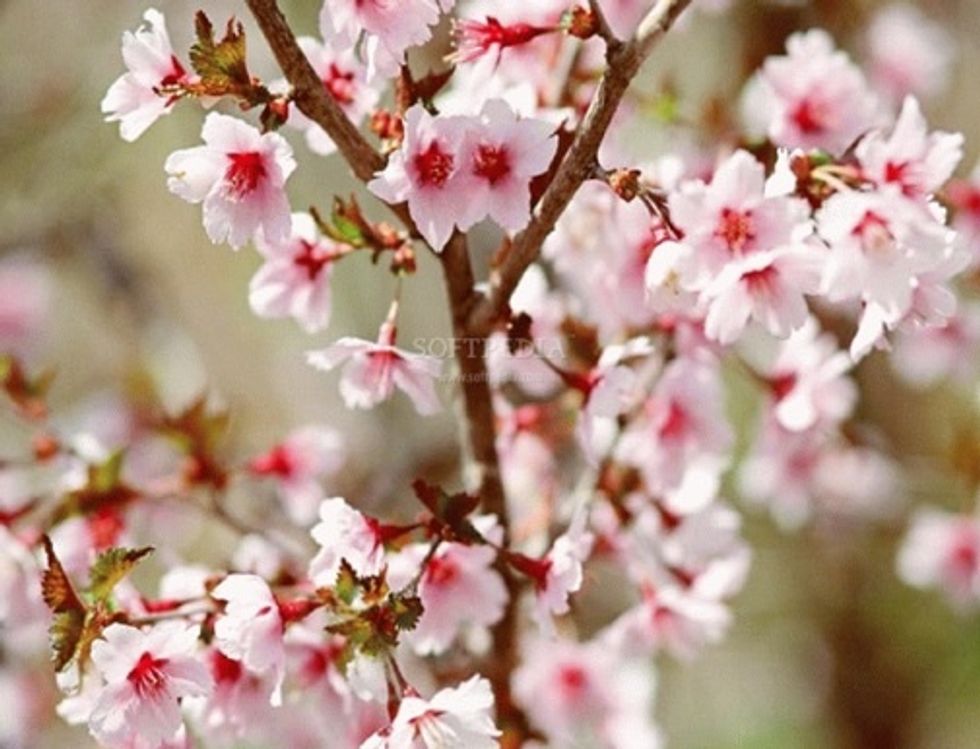
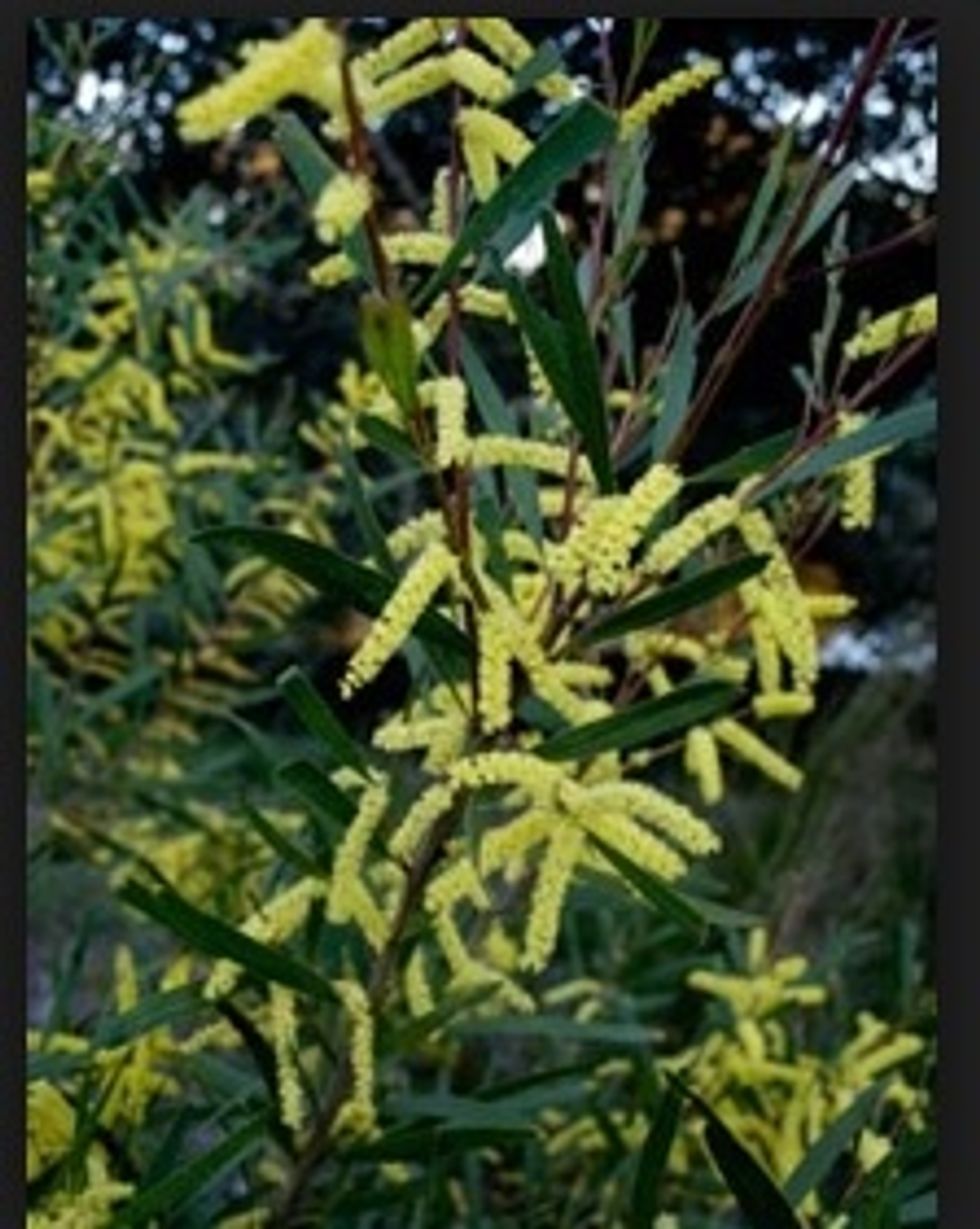


Wattle is a flowering plant common in Australia
Flowering plants can have leaves that alternate and have 'veins'. They include plants like herbs and orchids.
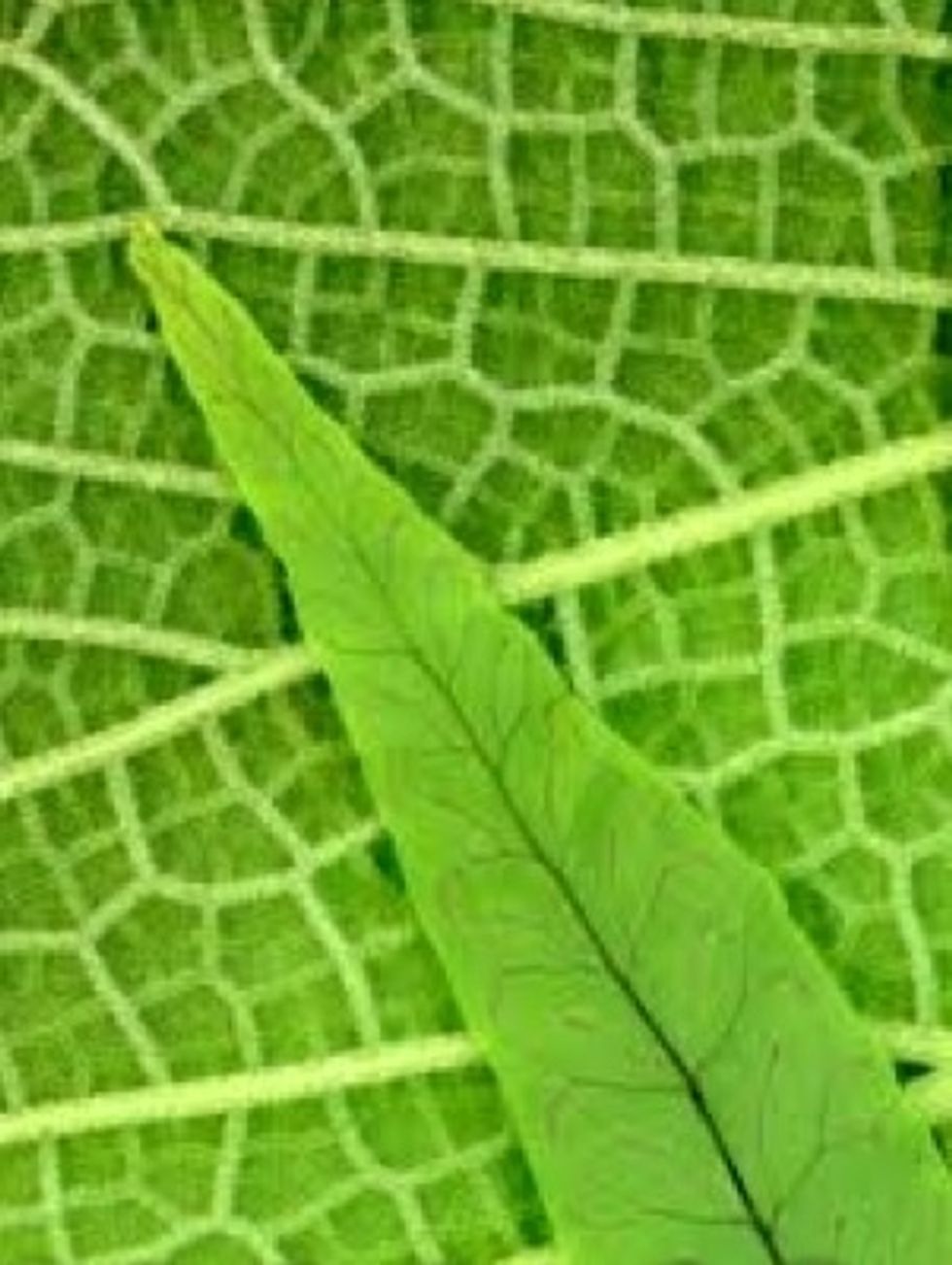
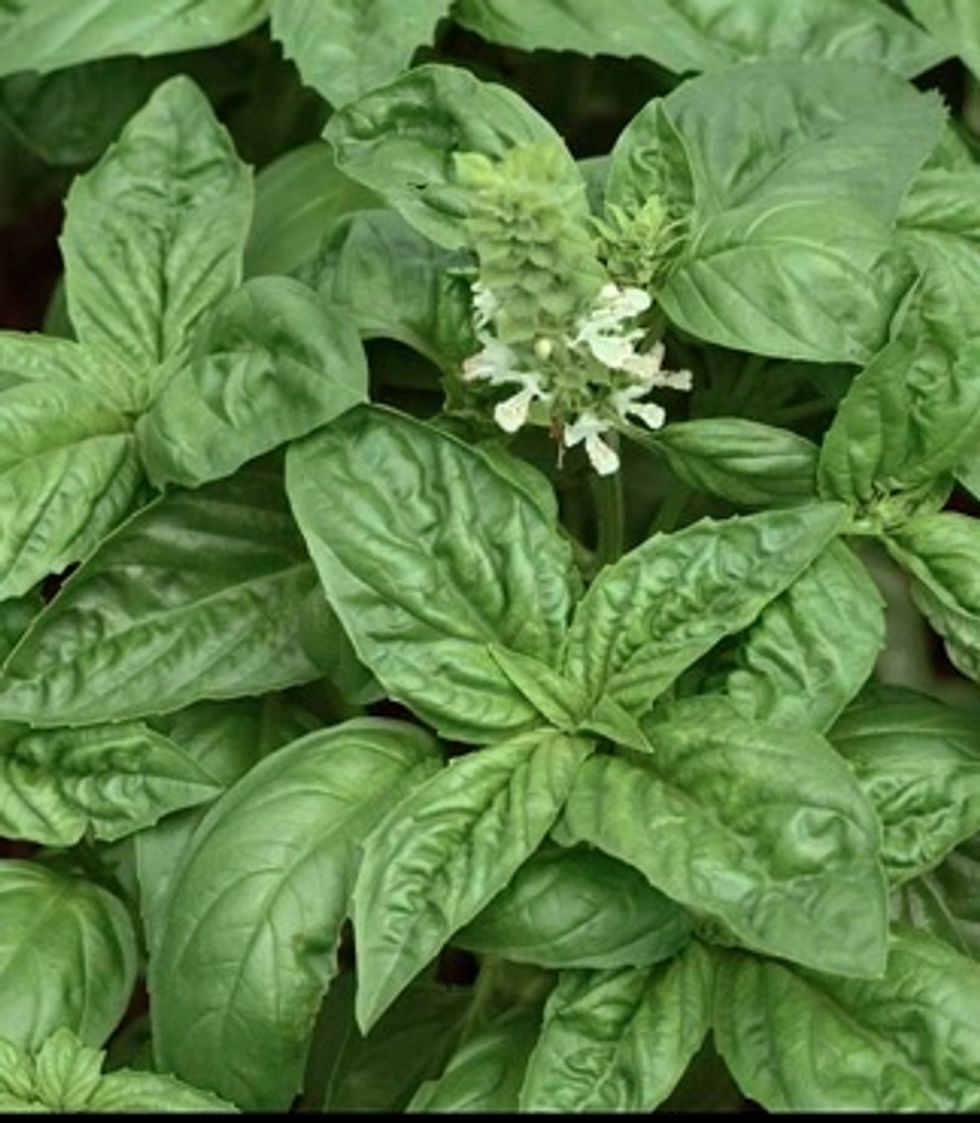
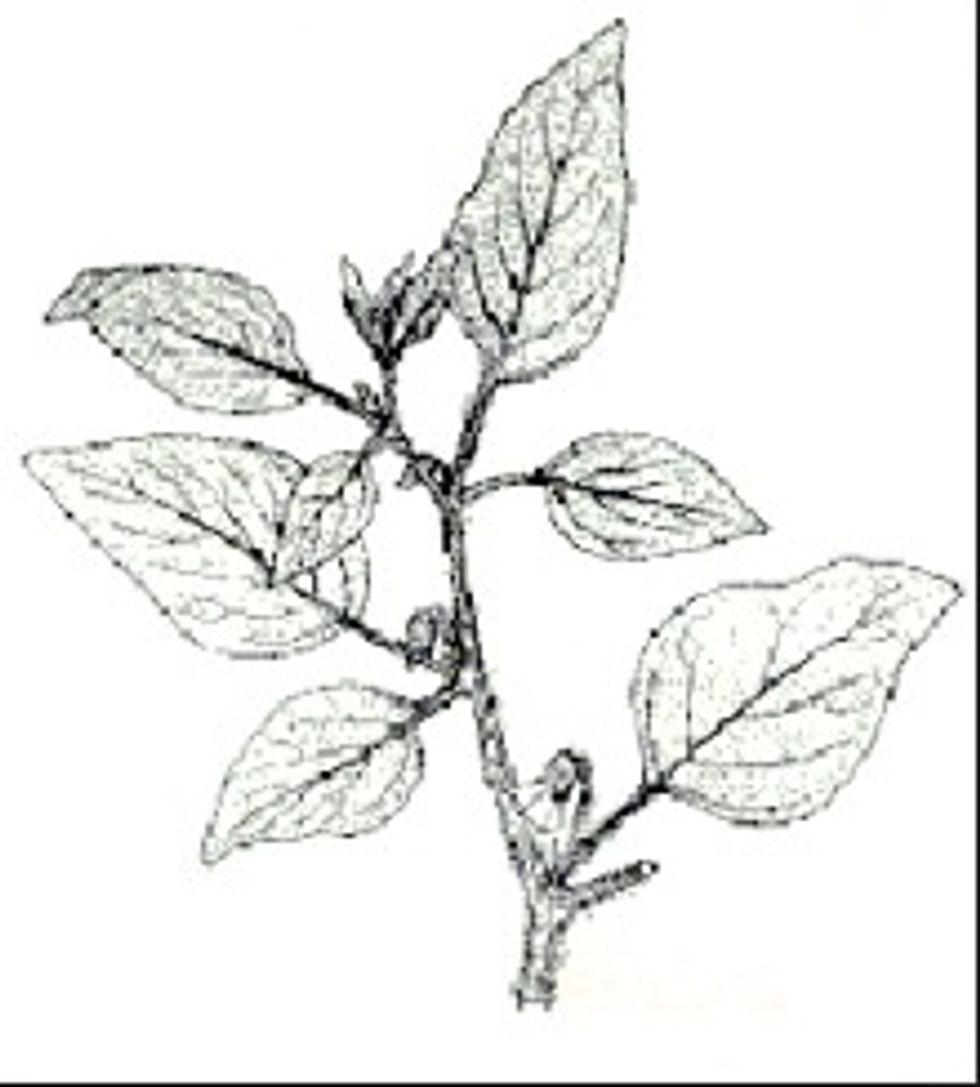


With flowering plants like basil we don't eat the flower - we eat the leaves
The end
- This guide
- An area of plants to classify
The Conversation (0)
Sign Up